Or try one of the following: 詹姆斯.com, adult swim, Afterdawn, Ajaxian, Andy Budd, Ask a Ninja, AtomEnabled.org, BBC News, BBC Arabic, BBC China, BBC Russia, Brent Simmons, Channel Frederator, CNN, Digg, Diggnation, Flickr, Google News, Google Video, Harvard Law, Hebrew Language, InfoWorld, iTunes, Japanese Language, Korean Language, mir.aculo.us, Movie Trailers, Newspond, Nick Bradbury, OK/Cancel, OS News, Phil Ringnalda, Photoshop Videocast, reddit, Romanian Language, Russian Language, Ryan Parman, Traditional Chinese Language, Technorati, Tim Bray, TUAW, TVgasm, UNEASYsilence, Web 2.0 Show, Windows Vista Blog, XKCD, Yahoo! News, You Tube, Zeldman
Eduexa
Educating Minds for an Empowering FutureST Full Form: Know meaning and how to apply for certificate 4 Jul 2025, 2:52 am
ST full form is Scheduled Tribes. These are the tribal or indigenous communities who have been designated or referred as “Scheduled Tribes” by the government of India. ST/SC/OBC/EWS are group of people who comes under the reserved category and the process of identification of each of these groups has been mentioned in the constitution for upliftment and progression of ST, SC, OBC and EWS. This detailed blog will discuss everything related to Scheduled tribe including ST full form, meaning, constitutional identification, certificate application as well as the benefits of ST.
What are Scheduled Tribes?
ST full form is Scheduled Tribe who are also commonly referred as Adivasis or indigenous peoples. These are simply the communities that have been designated as “Scheduled Tribes” by the government of India. These communities are primarily considered as primitive and often reside in forests. They are cut off from mainstream society and live in their own way. Because of being disconnected from the main society and advantages, they are entitled to certain protections and benefits under the Indian Constitution.
Scheduled Tribes are spread across different states in India and have their own distinct cultures, languages, and traditions. They often face challenges such as poverty, lack of access to education and healthcare, and discrimination. The government of India has implemented various programs and policies to address these issues and promote the socio-economic development of Scheduled Tribes.
Concept of Caste System in India
Indian Caste system is around thousands of years old which is a complex social hierarchy system, in which society divided into groups (castes or categories) based on their occupation, birth etc. It’s still prevalent in India with the main 4 Category or Caste System that are as follows:
- General Category (UR Category)
- OBC (Other Backward Classes)
- SC (Schedule Caste)
- ST (Schedule Tribe)
- EWS (Economically Weaker Sections)
ST Full Form in Hindi
The full form of ST in hindi is “अनुसूचित जनजाति“.
The term “Scheduled Tribes” comes from the Constitution of India, which lists certain tribal communities as being eligible for special treatment and protection under the law. These communities are referred to as “Scheduled Tribes” and are also known as “Adivasis” or “Indigenous Peoples.”
Implementation and Designation of Scheduled Tribe
Article 366 (25)
Article 366 (25) of the Constitution of India defines the Scheduled Tribes as “Such tribes or tribal communities or part of or groups within such tribes or tribal communities as are deemed under Article 342 to the Scheduled Tribes for the purposes of this [Indian] Constitution”.
Article 342
(1) The President may with respect to any State or Union Territory and where it is a State, after consultation with the Governor thereof by public notification, specify the tribes or tribal communities or parts of or groups within tribes or tribal communities which shall for the purpose of this Constitution be deemed to be Scheduled Tribes in relation to that State or Union Territory, as the case may be.
(2) Parliament may by law include in or exclude from the list of Scheduled Tribes specified in a notification issued under clause any tribe or tribal community or part of or group within any tribe or tribal community, but save as aforesaid a notification issued under the said clause shall not be varied by any subsequent notification.
Scheduled Tribes (STs) are identified based on indications of primitive traits, distinctive culture, geographical isolation, shyness of contact with the larger community, and overall backwardness.
History of ST (Scheduled Tribes)
Do you think reservation or ST categorisation was just any political move? No, it has a long history of discrimination, oppression, and marginalization. The ST or tribal communities in India have faced social and economic discrimination for centuries, and have often been treated as outcasts by the dominant castes in Indian society.
The STs are a diverse group of communities, each with its own distinct culture, language, and traditions. They are spread across the country and are found in almost every state and union territory in India. Many STs live in rural areas and engage in traditional occupations such as farming, forestry, and hunting and gathering.
In modern times, the Indian Constitution has recognized the STs as a distinct social group and has taken steps to address the historical discrimination and marginalization that they have faced. These steps include affirmative action programs such as reservation in education and employment, and the implementation of laws to protect the rights and dignity of STs.
“Check out the upcoming government exams in 2025″
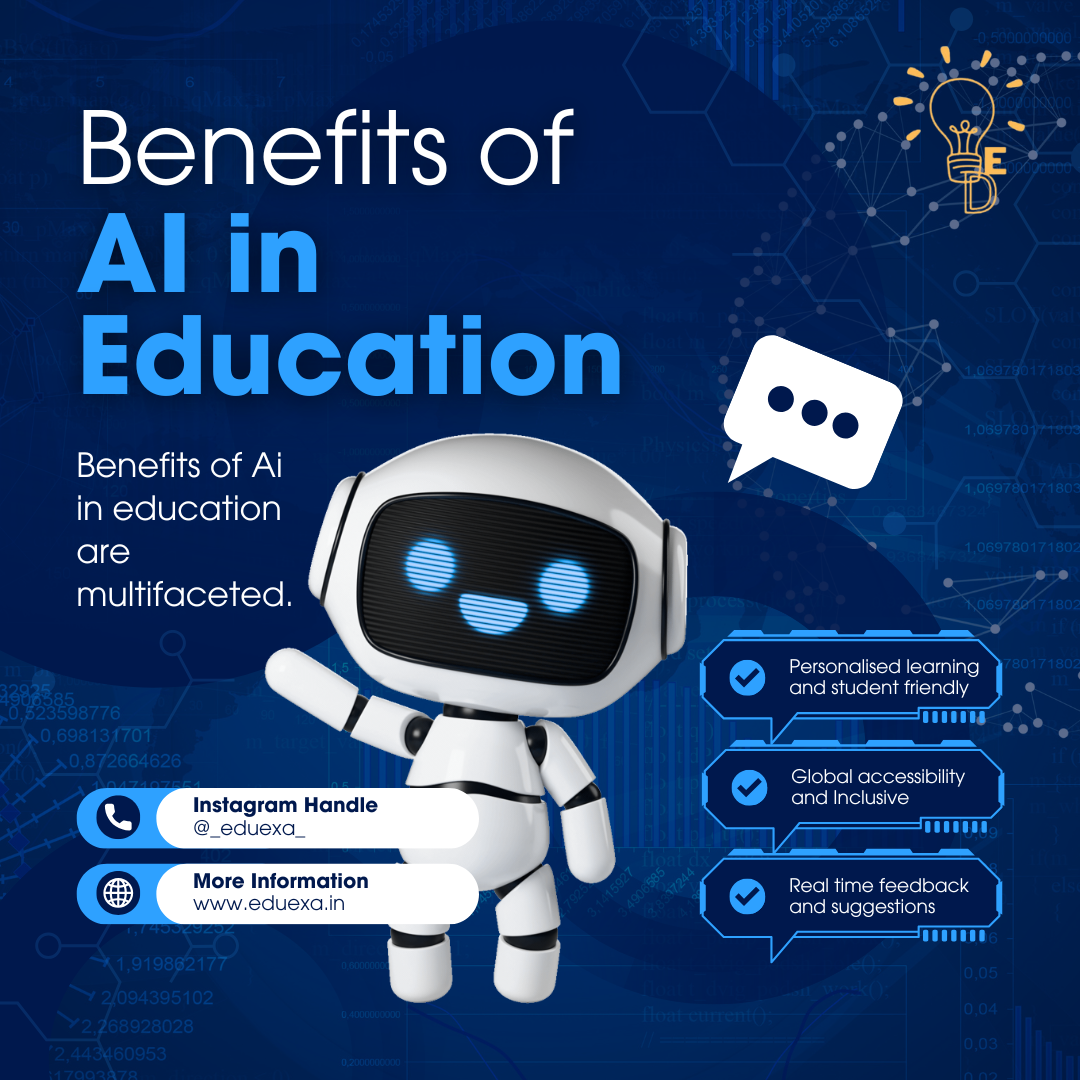
Benefits of ST (Scheduled Tribes)
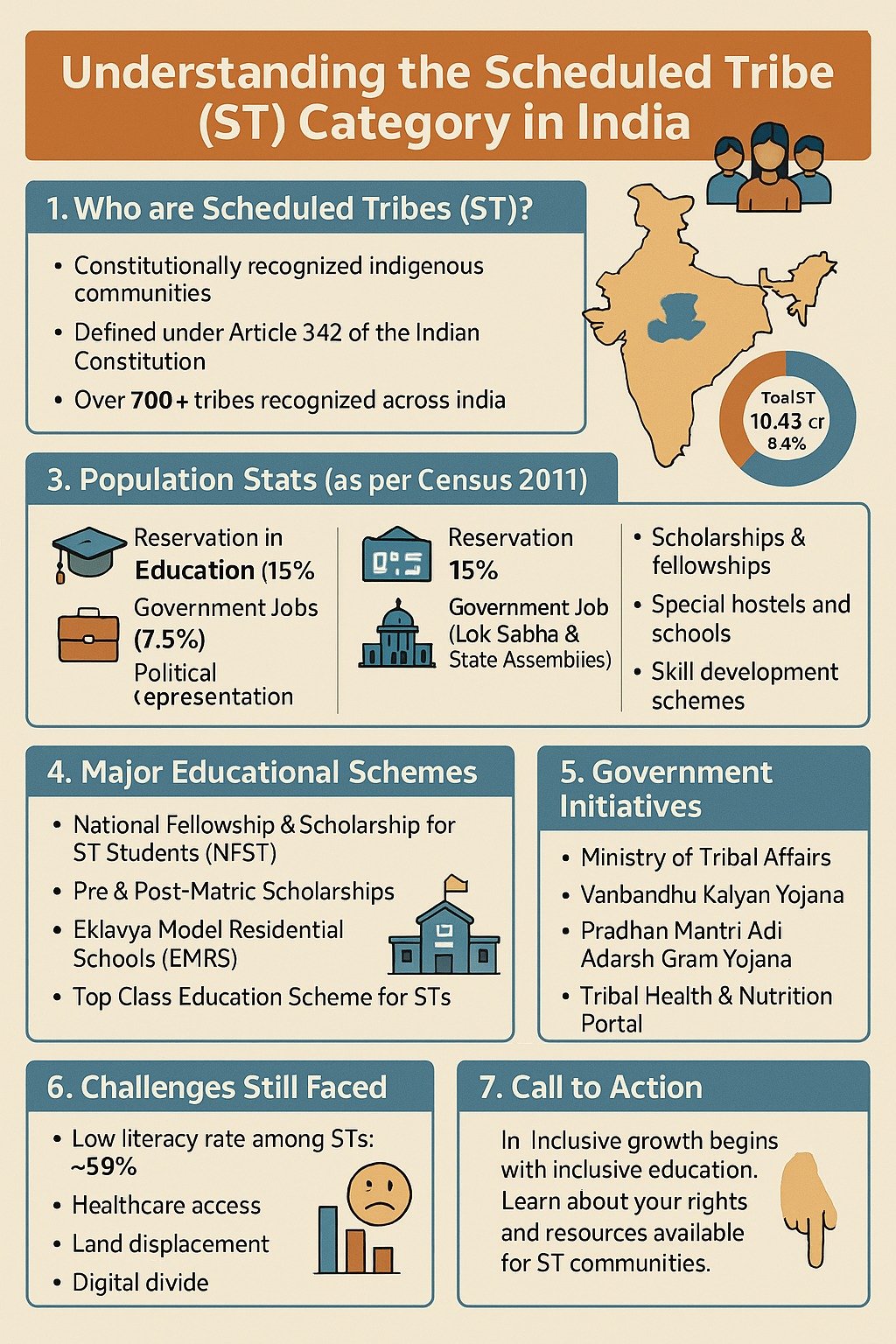
In India, Scheduled Tribes (STs) are socially and educationally disadvantaged groups that have been historically subjected to discrimination and oppression. The Indian Constitution provides for affirmative action measures to uplift these groups and ensure their inclusion and equality in society.
- One of the major benefits that people with ST category certificates receive is reservation of seats in educational institutions and government jobs. A certain proportion of seats are reserved for ST category that means these seats or vacancies can only be filled by the candidates under this category. As a results, they benefit by lower cut-offs at any stage of examination. The purpose of this measure is to ensure that STs have equal opportunities to access education and employment, and to help address the historical disadvantage faced by these groups.
- Not only the reservation of seats and jobs, STs are also eligible for various other benefits and schemes aimed at improving their socio-economic status. These benefits may vary ranging from financial assistance for education to subsidies for starting businesses to access to credit at lower interest rates.
- STs living in remote and tribal areas may also be eligible for special schemes and benefits aimed at improving their access to basic amenities such as healthcare, education, and clean drinking water.
National Commission for Scheduled Tribe
The National Commission for Scheduled Tribes (NCST) is a statutory body in India that was established under the provisions of the Constitution (89th Amendment) Act, 2003. This commission (i.e. NCST) is responsible for the protection, welfare, and development of Scheduled Tribes and it also takes possible actions and inquiry into any matter regarding deprivation of rights of the ST.
The NCST has a number of powers and functions to perform as discussed in the following section:
- To investigate and monitor all matters relating to the safeguards provided for Scheduled Tribes under the Constitution or any other law.
- To inquire into specific complaints regarding the deprivation of rights and safeguards of Scheduled Tribes.
- To participate and advise on the planning process of socio-economic development of Scheduled Tribes and to evaluate the progress of their development under the Union and any State.
- To present the reports about the working of those safeguards the President, annually and at such other times as the Commission may deem fit.
- To make recommendations for the effective implementation of those safeguards and other measures for the protection, welfare, and socio-economic development of Scheduled Tribes.
The NCST is headquartered in New Delhi and has regional offices in various states of India. It is composed of a Chairperson, Vice-Chairperson, and five other Members, all of whom are appointed by the President of India. The NCST operates under the Ministry of Tribal Affairs and works closely with other government agencies and non-governmental organizations to promote the welfare and development of Scheduled Tribes in India.
Documents Required to Get SC ST OBC Certificate
If you also fall under this category and still haven’t applied for the caste or category certificate it is important that you get your certificate for getting reservation benefits. If you are wondering what all documents are required to get EWS/SC/ST/OBC certificate To get an SC (Scheduled Caste), ST (Scheduled Tribe), or OBC (Other Backward Class) certificate in India, you will generally need to provide the following documents:
- Proof of identity: This could be a passport, PAN card, voter ID, or any other government-issued identification that has your photo, name, and address.
- Proof of residence: This could be a utility bill, rent agreement, or any other document that shows your current address.
- Birth certificate: This is required to prove your age and place of birth.
- Proof of caste: This could be a caste certificate issued by a competent authority, or a certificate issued by a previous employer, educational institution, or government agency that confirms your caste.
- Affidavit: You may need to provide an affidavit stating that you belong to the SC, ST, or OBC category and that you have not availed the benefits of reservation under this category before.
Note that the specific documents required may vary depending on the state in which you are applying for the certificate and the category for which you are applying. It is best to check with the local authorities or the office responsible for issuing SC, ST, or OBC certificates for the exact requirements.
Difference Between SC and ST
While both the categories are reserved categories, they are not the similar categories. SC and ST are abbreviations for Scheduled Caste and Scheduled Tribe, respectively. These are official terms used in the Indian Constitution to refer to certain historically disadvantaged social groups.
| SC | ST | |
| Full form | SC Full form is Scheduled Caste | ST full form is Scheduled Tribe |
| Meaning | The Scheduled Castes are a group of communities or castes which are considered as being socially and economically disadvantaged because of historical designation as outcastes from the Hindu caste system. | The Scheduled Tribes are indigenous communities that have a distinctive culture, language, and way of life. |
| Classification | SC or Scheduled Castes are considered to be a part of the Hindu social system. | Whereas ST are considered to be distinct indigenous communities with their own cultural and social practices. |
| Articles | Article 366 (24) of the Constitution of India defines the Scheduled Castes as:
Such castes, races or tribes or part of or groups within such castes, races or tribes as are deemed under Article 341 to be Scheduled Castes for the purpose of this [Indian] constitution. |
Article 366 (25) of the Constitution of India defines the Scheduled Tribes as “Such tribes or tribal communities or part of or groups within such tribes or tribal communities as are deemed under Article 342 to the Scheduled Tribes for the purposes of this [Indian] Constitution”. |
Reservation System in India

In India, there are various types of reservation systems in place for various purposes. Here are some examples:
- Educational institutions: Many educational institutions in India like Delhi University etc. have a reservation system for admissions where the cut offs for each category differs. This reservation is based on factors such as caste, religion, and nationality.
- Government jobs: Another place where reservations exist is the government jobs. Almost every government exam like those conducted by UPSC, SSC etc have different relaxations for people belonging to SC, ST, OBC and EWS. This reservation is based on factors such as caste, religion, and nationality.
- Political representation: The Indian constitution provides for reservation of seats in the parliament and state legislative assemblies for Scheduled Castes (SCs) and Scheduled Tribes (STs). This reservation is aimed at providing representation to these historically disadvantaged groups. Further, Nari Shakti vandan Act 2024 has provided for reservations for women in Lok sabha and state assemblies.
- Public transportation: Some states in India have a reservation system for certain categories of passengers on public transportation, such as buses and trains. This reservation is based on factors such as age, disability, and military service.
- Housing: Some states in India have a reservation system for housing, which provides certain categories of people with priority in the allocation of government-owned housing.
Overall, the reservation systems in India are meant to address historical imbalances and ensure that certain groups have equal opportunities in various fields. However, there has been much debate and controversy surrounding these systems, with some people arguing that they are necessary to address historical injustices and others arguing that they are unfair and create divisions within society.
List of Scheduled Tribes
Scheduled tribes are groups of people who have been formally recognized by the government of India as being socially and economically disadvantaged and in need of special protection and support. There are a total of 705 scheduled tribes in India. Here is a list of some of the major scheduled tribes in India:
- Adivasis: This is a broad term used to refer to indigenous communities in India. Adivasis are found in many states of India, including Andhra Pradesh, Gujarat, Jharkhand, Maharashtra, and Odisha.
- Bhils: This is a large tribal group found in the states of Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, and Maharashtra.
- Gonds: This is a tribal group found in the states of Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Maharashtra, Telangana, and Andhra Pradesh.
- Santhals: This is a tribal group found in the states of Jharkhand, West Bengal, Odisha, and Bihar.
- Mundas: This is a tribal group found in the states of Jharkhand, Odisha, and West Bengal.
- Oraons: This is a tribal group found in the states of Jharkhand and Odisha.
- Kondhs: This is a tribal group found in the states of Odisha and Andhra Pradesh.
This is just a small sampling of the scheduled tribes in India. There are many other tribal groups found in different parts of the country, each with its own unique culture, language, and traditions.
Conclusion
This comprehensive guide has covered all the sections related to Scheduled Tribes starting from ST full form to historical perspective to present day benefits. Further the classification and difference between SC and ST has been elaborated for better clarity. Now that you have understood about the category and certificate application, it is essential to get the certificate to claim the reservation.
FAQs
1. What is ST full form?
ST full form in English is scheduled tribes whereas in Hindi it is “अनुसूचित जनजाति”.
2. What is meant by ST caste?
ST category stands for the communities that are indigenous tribes of India which are considered primitive and distant from the mainstream.
3. Which caste is the ST category?
The castes or communities that are officially designated as “Scheduled Tribe” under article 342 for the purpose of the Indian Constitution are considered as ST.
4. What are SC, ST and OBC?
SC stands for scheduled Castes, ST stands for Scheduled Tribes and OBC stands for Other Backward Class.
The post ST Full Form: Know meaning and how to apply for certificate appeared first on Eduexa.
IBPS PO 2025 Notification Out – Apply Now for 5208 Vacancies 2 Jul 2025, 6:31 am
The much awaited IBPS PO 2025 notification is now out, opening vacancies for 5208 positions across different public sector banks. Registration began from 1st of July 2025, apply at the earliest to avoid any delays and inconveniences and secure a position in India’s leading public sector banks. This comprehensive guide covers everything from the IBPS PO 2025 application process to the IBPS PO syllabus, eligibility criteria, exam pattern, important dates, and more. If you are serious about cracking the IBPS PO banking exam, read on and apply online for IBPS PO 2025 without any delay.
IBPS PO Notification
The Institute of Banking Personnel Selection (IBPS) is the autonomous body which assists the organisation with selection of personnel at different organisational levels. It has released the much-awaited IBPS PO 2025 notification, inviting applications for Probationary Officer (PO)/Management Trainee (MT) posts. IBPS conducts this recruitment drive annually to select deserving candidates for the post of Probationary Officer/Management Trainee in public sector banks.
| Particulars | Details |
| Exam Name | IBPS PO 2025 |
| Conducting Body | Institute of Banking Personnel Selection (IBPS) |
| Post Name | Probationary Officer / Management Trainee |
| Number of Vacancies | 5208 (Tentative) |
| Application Mode | Online |
| Exam Mode | Online (Prelims & Mains) |
| Official Website | www.ibps.in |
IBPS PO 2025 Important Dates
Candidates must keep track of all crucial dates related to IBPS PO 2025 to avoid missing deadlines. Some of the key dates are mentioned below:-
| Event | Date |
| IBPS PO 2025 Notification Release | 1 July 2025 |
| Online Registration Start Date | 1 July 2025 |
| Last Date to Apply | 21 July 2025 |
| Last Date for printing your application | 5 August 2025 |
| Payment of Application Fees | 1-21 July 2025 |
| IBPS PO Prelims Admit Card | – |
| IBPS PO Prelims Exam Date | 17, 23, 24 August |
| IBPS PO Mains Admit Card | – |
| IBPS PO Mains Exam Date | – |
| Interview | – |
| Final Result | – |
“RRB 2025 notification is out- Read about RRB exams 2025“
IBPS PO 2025 Registration – How to Apply Online?
The IBPS PO 2025 registration process is completely online. Follow these steps to apply successfully.

Step-by-Step Guide to Apply Online
- Visit the official IBPS website: www.ibps.in
- Click on “CRP PO/MT” and then select “IBPS PO 2025 Apply Online”.
- Register using a valid email ID and mobile number.
- Fill in your personal, educational, and communication details.
- Upload the required documents including photograph, signature, thumb impression, and handwritten declaration.
- Pay the application fee using online payment options.
- Submit the application and download a copy for your records.
Application Fees
- General/OBC candidates: ₹850
- SC/ST/PwD candidates: ₹175
“Preparing for government exams? Never miss out on any upcoming government exam notification”
IBPS PO 2025 Eligibility Criteria
Before proceeding with the registration, it is important to make sure that you fulfill all the IBPS PO eligibility requirements from age limits to educational qualifications. The eligibility criteria for the IBPS PO exam are as follows:
Nationality
- You must be an Indian citizen
OR
- A subject of Nepal, Bhutan, or a Tibetan refugee who came to India before January 1, 1962
OR
- Persons of Indian origin who migrated from select countries (as per IBPS guidelines)
Educational Qualification
- A graduate degree in any discipline from a recognized university is mandatory
- Final-year students can also apply, provided they meet eligibility by the final document verification stage.
Age Limit (as of August 1, 2025)
- Minimum age: 20 years
- Maximum age: 30 years
- Age relaxation applies for reserved categories according to government norms.
IBPS PO 2025 Exam Pattern
As per IBPS PO 2025 notification, PO exam will be conducted in three stages: Preliminary stage, Main exam and Interview round.
Preliminary Exam
| Section | No. of Questions | Marks | Duration |
| English Language | 30 | 30 | 20 minutes |
| Quantitative Aptitude | 35 | 35 | 20 minutes |
| Reasoning Ability | 35 | 35 | 20 minutes |
| Total | 100 | 100 | 60 minutes |
Main Exam
| Section | No. of Questions | Marks | Duration |
| Reasoning & Computer Aptitude | 45 | 60 | 60 minutes |
| General/Economy/Banking Awareness | 40 | 40 | 35 minutes |
| English Language | 35 | 40 | 40 minutes |
| Data Analysis & Interpretation | 35 | 60 | 45 minutes |
| Descriptive (Essay & Letter Writing) | 2 | 25 | 30 minutes |
| Total | 157 | 225 | 3 hours 30 minutes |
Interview
- Conducted for candidates who qualify the Mains exam.
- Interview is of 100 marks.
- Minimum qualifying marks: 40 percent (35 percent for reserved).
IBPS PO 2025 Syllabus
A deep understanding of the IBPS PO syllabus is essential for success.
| IBPS PO Syllabus | ||
| English Language |
|
|
| Quantitative Aptitude |
|
|
| Reasoning Ability |
|
|
| General Awareness |
|
|
| Computer Aptitude |
|
|
Participating Banks
IBPS PO exam is conducted to fill the vacancies for the post of PO or MT across participating public sector banks. 11 banks are part of IBPS and the candidates are recruited to work for one of these 11 participating banks.
| Participating Banks | |
| Bank of Baroda | Bank of India |
| Bank of Maharashtra | Canara Bank |
| Central Bank of India | Indian Bank |
| Indian Overseas Bank | Punjab National Bank (PNB) |
| Punjab & Sind Bank | UCO Bank |
| Union Bank of India | |
Why You Should Apply for IBPS PO 2025?

The IBPS PO 2025 recruitment offers a stable and rewarding career in the banking sector. Candidates selected as Probationary Officers will get to work in top public sector banks such as Bank of Baroda, Canara Bank, Bank of India, Union Bank of India etc. Apart from the experience of working with prestigious institutions, there are other key perks that you will get after clearing IBPS PO 2025 exam.
Attractive salary package and perks
Just like any other government job, this PO position also offers attractive salary. I hope you are aware of the initial in-hand salary of an IBPS Probationary Officer. If not, let me tell you, it is Rs. 74,000 to 76,000 with dearness allowances, special allowances, and other benefits. The basic pay scale of a PO is Rs. 48480-2000/7-62480-2340/2-67160-2680/7-85920 as per the revision made to the salary.
Job security with pension benefits
The major reason or perks of a government job like IBPS PO is job security. Market fluctuations and profit reduction can not result in lay off or permanent termination. Your job is secure from any external emergencies or situations as well as it is also securing your future with adequate pensions and employee benefits.
Nationwide job postings
One of the most interesting and unique aspects of the Probationary Officer role is the opportunity to serve and work from any part of the country. You can be posted to any city, town, rural area and even remote regions. This way you not only experience the diverse cultures and lifestyle but also build an adaptable and resilient personality positive for your career progression.
Fast career progression through internal promotions
You can fast progress your career by this role sequence:-
Probationary Officer → Assistant Manager → Branch Manager → Senior Manager → Chief Manager → Assistant General Manager → Deputy General Manager → General Manager → Executive Director/Chairman & Managing Director (in rare but possible cases)
Work-life balance and social respect
People have this perception that banking jobs are quite demanding but the reality is public sector banks are more structured and regulated compared to the private sector, which translates into fixed working hours, scheduled holidays, entitled leaves etc. All this contributes to maintaining better work life balance.
Preparation Tips for IBPS PO 2025
Follow a dedicated daily study plan: A timetable and proper study plan is a must to have well-defined daily goals and targets. When you have a roadmap, you can also track your progress well and restructure your preparation when it does not go in the same flow with your study plan.
Start with basics: The most common mistake that students make is to start learning or advancing to higher level of questions or difficult parts of the syllabus. But this approach does not give results because if you are struggling with the basics, advanced level understanding would be hard to develop. So it is better to work on conceptual clarity first and gradually take up advanced-level practice.
Solve PYQs and online mock tests: Previous year papers are the backbone of your preparation. These papers do not just give you an idea about paper pattern but it also gives you insights on frequently asked questions. Further, attempting online mock tests gives you feedback on your preparation and prepares you for all types of questions and format
Work on the English Section: The English Language section is often underestimated, but it plays a critical role in both prelims and mains. Developing reading comprehension skills and vocabulary will definitely give you an edge over other students.
Current Affairs: Another important aspect of IBPS PO 2025 exam preparation is staying updated with current affairs and banking news. A lot of questions are asked from the latest news related to banking be it on rates, chairman or simply numeric investments.
“Finding it difficult to stay focused? Learn about some simple techniques to find motivation to study”
Conclusion
The IBPS PO 2025 exam is one of the most sought-after opportunities for banking aspirants in India. With attractive pay, job stability, and growth potential, it offers a promising future for young professionals. The IBPS PO 2025 registration is now open, and the sooner you apply and start preparing, the better your chances of selection.
For more updates on banking exams, stay tuned to our blog and start your preparation for IBPS PO 2025 today.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) – IBPS PO 2025
Q1. When will IBPS PO 2025 registration start?
The registration for IBPS PO 2025 is expected to begin in July 2025. The official notification has been released on the IBPS website.
Q2. What is the last date to apply for IBPS PO 2025?
The last date to apply online is 21 July 2025. Candidates should also check the official website regularly for any extension of the last date.
Q3. What is the eligibility for IBPS PO 2025?
Candidates must hold a graduate degree from a recognized university and be between 20 to 30 years of age.
Q4. Is there any negative marking in IBPS PO exam?
Yes, 0.25 marks will be deducted for each incorrect answer in both the Preliminary and Mains exams.
Q5. What is the salary of an IBPS PO?
The initial basic pay for an IBPS PO is around ₹36,000–₹42,000, excluding additional allowances, which can take the monthly salary to ₹52,000–₹55,000 or more depending on the location.
Q6. Can final-year students apply for IBPS PO 2025?
Yes, final-year students can apply, but they must produce proof of graduation during the document verification stage.
Q7. What are the subjects included in the IBPS PO syllabus?
The syllabus includes English Language, Quantitative Aptitude, Reasoning Ability, General Awareness (with Banking), and Computer Aptitude.
Q8. Is IBPS PO a government job?
Yes, IBPS PO is a government job in public sector banks regulated by the Government of India and RBI.
Q9. Is the fees for women candidates waived off?
No, all the candidates irrespective of his/her gender has to pay the examination fee.
The post IBPS PO 2025 Notification Out – Apply Now for 5208 Vacancies appeared first on Eduexa.
NEET PG 2025: Check the Admit Card and Exam Dates 1 Jul 2025, 2:18 pm
Are you planning to appear for one of the most competitive and toughest medical entrance test in India? I mean NEET PG 2025. The National Eligibility cum Entrance Test for Postgraduate (NEET PG) has been scheduled on 3rd of August 2025 (earlier scheduled for 15th June). NEET PG serves as the gateway to MD/MS/PG Diploma courses in top government and private medical colleges across the country.
This comprehensive guide will help you stay updated with the NEET 2025 exam date, eligibility, registration details, and a thorough breakdown of the previous and expected cut offs.
NEET PG 2025 Exam Date
The NEET PG 2025 exam date has been revised to 3 August 2025 from earlier 15 June 2025. Neet PG is being conducted by the National Board of Examinations in Medical Sciences (NBEMS) which is also responsible for releasing the exam dates and results. Based on the notification, exam schedule and admit card release dates are mentioned below:
| Event | Date |
| City Intimation | 21st July 2025 |
| Admit Card Release | 31st July 2025 |
| NEET PG 2025 Exam Date | 3rd April 2025 |
| Result Announcement | – |
| Counselling Begins | – |
🔔 Note: Always refer to the official NBEMS website for the latest updates on NEET PG entrance exam 2025.
NEET PG admit card
Candidates who have successfully applied for NEET PG 2025 can download their admit cards from the official website of NBE. NBE will activate NEET PG admit card 2025 link online on 31st July 2025 as per the revised schedule. Candidates will be able to select fresh test city from the list provided by NBE. NBE reopened the application window to choose test city from June 13 to June 17, 2025. It must be noted that admit card for NEET PG 2025 will not be sent to individual candidates. Each aspirant need to download NEET PG hall ticket 2025 from the official website of NBE, nbe.edu.in through application ID and password. A direct link will be provided on this page to download NEET PG 2025 admit card.
“Also check out the list of upcoming government exam in 2025″
How To Download NEET PG 2025 Admit Card?
 Candidates who are going to appear for the NEET PG 2025 can avail the admit cards from the official website of the National Board of Examinations (NBE). Candidates can check the following steps to download the NEET PG 2025 admit card below:
Candidates who are going to appear for the NEET PG 2025 can avail the admit cards from the official website of the National Board of Examinations (NBE). Candidates can check the following steps to download the NEET PG 2025 admit card below:
Step 1: Firstly, candidates need to visit the official National Board of Examinations (NBE) official website.
Step 2: Now you need to find the “NEET PG Tab” and click on the “NEET PG Admit Card” Link.
Step 3: NEET PG Admit Card download – Login by entering user name/ ID and password to download the NEET PG 2025 Admit Card.
NOTE:- In case you have forgotten your login details you can reset it from the official website.
Step 4: NEET PG 2025 admit card will appear on the screen.
Step 5: The candidate should download and take a printout of the NEET PG admit card for future reference.
Note: NEET PG photograph should be of the following specifications, without which, it will not be printed in the admit card:
- Size of photograph: Not less than 35×45 mm (and not larger than the box printed on the admit card for pasting the photograph). The photo must have 75% coverage of the face & head of the candidate.
- It must be a colour photograph on a white background.
- The photo should show a full front view of the face and must have a neutral expression. No caps, stethoscopes, goggles or ornaments are allowed.
- There should not be any reflection, shadow on the face, or red eyes.
- The picture must be printed on Photo Paper with at least 600 dpi Resolution.
- No bends, scratches, fingerprints, or stains should be present on the photograph.
Details Mentioned On NEET PG Admit Card 2025
The NEET PG Admit Card not only contains the details of the examination but it also has complete information of the candidate. The following details are mentioned in the NEET PG 2025 admit card:
- Registration
- Number of the candidate
- Name of the candidate, Parent’s /guardian’s name
- Roll number of the candidate
- Details of the exam venue
- Time of exam
- Subject for which the exam is to be taken
- Medium/ Language for the exam
- Slot wise division of the exam
- Exam Day Instructions
NEET PG 2025 Syllabus
The NEET PG syllabus is based on the curriculum taught during the MBBS course prescribed by the National Medical Commission (NMC). It includes topics from Pre-clinical, Para-clinical, and Clinical subjects.
1. Pre-Clinical Subjects
- Anatomy
- Physiology
- Biochemistry
2. Para-Clinical Subjects
- Pathology
- Pharmacology
- Microbiology
- Forensic Medicine
- Social and Preventive Medicine (SPM)/Community Medicine
3. Clinical Subjects
- General Medicine (including Dermatology, Psychiatry)
- General Surgery (including Orthopaedics, Anaesthesia, Radiology)
- Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- Paediatrics
- ENT
- Ophthalmology
Pro Tip: Focus on high-yield topics from Medicine, Surgery, and OBGYN as they carry significant weight in the NEET PG entrance exam.
NEET PG 2025 Exam Pattern
Understanding the paper pattern is crucial for your preparation. Here’s what you need to know:
| Parameter | Details |
| Mode | Computer-Based Test (CBT) |
| Duration | 3 hours 30 minutes |
| Number of Questions | 200 Multiple Choice Questions |
| Total Marks | 800 |
| Marking Scheme | +4 for correct, -1 for incorrect |
| Language | English |
Eligibility Criteria for NEET PG 2025
To apply for NEET PG 2025, candidates must fulfill the following criteria:
- Educational Qualification: MBBS degree or provisional pass certificate recognized by the NMC.
- Internship Completion: Must have completed a 12-month rotatory internship by March 31, 2025.
- Registration: Must have a valid provisional/permanent registration with NMC or State Medical Council.
NEET PG 2025 Registration Process
The application process for NEET PG 2025 will be conducted online. Follow these steps to register:
Step-by-Step Guide:
- Visit nbe.edu.in or natboard.edu.in
- Register using email ID and phone number
- Fill in academic and personal details
- Upload scanned documents (photo, signature, thumb impression)
- Pay the application fee online
- Submit and download the confirmation page
Application Fee (Based on NEET PG 2024)
| Category | Fee |
| General/OBC | ₹4250 |
| SC/ST/PwD | ₹3250 |
NEET PG 2025 Cut-Off (Expected)
 The cut-off marks depend on factors like exam difficulty and number of applicants. Here’s the expected range:
The cut-off marks depend on factors like exam difficulty and number of applicants. Here’s the expected range:
| Category | Minimum Qualifying Percentile | Expected Cut-off (Out of 800) |
| General | 50th | 280 – 320 |
| SC/ST/OBC | 40th | 240 – 280 |
| PwD (General) | 45th | 260 – 300 |
NEET PG vs NEXT – What to Expect?
There has been discussion about replacing NEET PG with the National Exit Test (NEXT). However, as of now, NEET PG 2025 will continue to be conducted as per NBEMS regulations.
Always verify any policy change from official government sources before relying on news articles or social media.
Tips for the exam day
The day of the exam is the actual deciding moment for you. This day decides whether you will clear the exam or not and hence it is important that you do not mess anything up on this day. The year-long preparation can be turned into life long success by engaging in simple steps and avoiding minor mistakes.
General Tips
- Do not engage in last minute revision
- Avoid discussing the exam topics/preparation etc or simply saying do not get into any conversation with your classmates starting with “Tune ye topic dekha tha” etc. Not knowing the topic might lead to additional stress and anxiety.
- Stay calm and peaceful- Being impatient and nervous can impact your performance
- Check the location of your exam centre and if possible visit the centre after you get your admit card to avoid any confusion on the exam day.
- When heading to the exam center, leave a bit earlier to account for any last-minute delays or mishappenings, ensuring you arrive on time.
- Print 2-3 hard copies of the admit card so that you do not lose it at the last minute.
- Carefully read the instructions mentioned in the admit card.
Examination Hall tips
The candidates must strictly follow the below guidelines during the NEET PG examination to avoid stepping into troubling matters:
- The candidates should not carry any study material inside the NEET PG examination hall for last-minute revision.
- The aspirants are restricted from carrying any digital devices like mobiles, calculators, or smartwatches to the NEET PG Exam hall.
- The candidate must manage the timetable accordingly during the time of the NEET PG Examination.
- Fill all the details correctly in the sheet and recheck it again for assurance.
- Thoroughly read the question paper and attempt carefully.
Final Thoughts
The NEET PG 2025 exam is your stepping stone toward a successful medical postgraduate career. Being aware of the neet pg syllabus, neet 2025 exam date, and exam strategy is key to cracking this competitive exam. Stay updated, stay consistent, and believe in your preparation journey.
“Bookmark this page for all the latest updates on NEET EXAM 2025 including official notifications, exam pattern, and study resources.”
Common Questions
How To Download NEET PG 2025 Admit Card If You Do Not Have Access To The Internet?
You can download the NEET PG 2025 admit card from the official website of NBE. In case you do not have a stable internet or no internet access then you should visit a nearby cyber cafe, where they can follow the necessary steps to download and print your admit card.
What If Candidates Misplace Their NEET PG 2025 Admit Card?
I know most of us do not find our important stuff in the time of need. In case you misplace your NEET PG 2025 admit card, you need not panic. At such time, just log in to the official website of NBE at https://natboard.edu.in then re-download and print your admit card. It is important to keep 2 to 3 hard copies of the admit card for the exam.
Thing To Carry On NEET PG Exam Day
Candidates need to carry the following important documents and materials to the examination hall for the NEET PG 2025 examination:
- NEET PG 2025 Admit Card (mandatory)
- Original Photo ID proof (mandatory)
The following documents can be accepted as photo ID proof in the NEET PG Exam Hall:
- Driving license
- Aadhar card
- PAN Card
- Voter id card
- Passport
What things are not allowed on NEET PG exam day? Things Not To Carry On NEET PG Exam Day
The candidate should refrain from bringing any items that are strictly restricted by the NEET PG as mentioned below:
- Mobile phones
- Calculators
- Smartwatches
- Study material
- Bags
The post NEET PG 2025: Check the Admit Card and Exam Dates appeared first on Eduexa.
SSC CGL Syllabus 2025: Check out updated preparation guide 27 Jun 2025, 6:54 am
Exam notification is out and now it’s high time that you gear up your preparation with the latest SSC CGL Syllabus 2025, key exam guidelines and detailed understanding of the exam pattern. Perfect exam preparation starts with understanding the updated exam syllabus and ends with consistent efforts to crack the exam.
SSC CGL 2025 Exam Pattern: A Detailed Breakdown
The SSC CGL exams is of 4 tiers each tier assess different skill sets, here is the detailed breakdown of SSC CGL 2025 Exam Pattern-
Tier 1: Computer-Based Examination (Objective Type)
This is the first screening stage in SSC CGL exam 2025 and is compulsory for all applicants. This stage is a computer based test conducted for a duration of 1 hr assessing the skills over different sections- General Intelligence & Reasoning, general awareness, quantitative aptitude and English comprehension.
| Section | No. of Questions | Maximum Marks | Time Allotted |
| General Intelligence & Reasoning | 25 | 50 | |
| General Awareness | 25 | 50 | |
| Quantitative Aptitude | 25 | 50 | |
| English Comprehension | 25 | 50 | |
| Total | 100 | 200 | 60 minutes |
Negative Marking: 0.50 marks deducted for each wrong answer.
Mode: Computer-based test (CBT).
Tier 2: Computer-Based Examination (Objective Type)
This stage is more comprehensive and post-specific, consisting of four papers.
| Paper | Subject | No. of Questions | Maximum Marks | Time Allotted |
| Paper 1 | Quantitative Abilities | 100 | 200 | 2 hours |
| Paper 2 | English Language and Comprehension | 200 | 200 | 2 hours |
| Paper 3 | Statistics (for JSO) | 100 | 200 | 2 hours |
| Paper 4 | General Studies (Finance & Economics) (AAO) | 100 | 200 | 2 hours |
Note:
- Paper 1 and Paper 2 are compulsory for all candidates.
- Paper 3 is only for candidates who applied for Junior Statistical Officer (JSO).
- Paper 4 is only for candidates who applied for Assistant Audit Officer/Assistant Accounts Officer (AAO).
Negative Marking:
- Paper 1, 3, 4: 0.50 marks for each wrong answer.
- Paper 2: 0.25 marks for each wrong answer.
Tier 3: Descriptive Paper (Pen & Paper Mode)
This stage tests your writing skills, which are crucial for many government posts.
| Paper | Details |
| Mode | Pen and paper (Offline) |
| Type | Descriptive (Essay, Letter, Application Writing) |
| Language | English or Hindi |
| Maximum Marks | 100 |
| Duration | 60 minutes |
Note: Tier 3 is qualifying in nature, but the marks are added to the final merit list.
Tier 4: Skill Test/Document Verification
This stage is post-specific and assesses practical skills required for certain positions:
Data Entry Speed Test (DEST):
- For Tax Assistant posts.
- Requires a typing speed of 8,000 key depressions per hour on the computer.
Computer Proficiency Test (CPT):
- For certain Assistant Section Officer posts (CSS, MEA, etc.).
- Includes proficiency in Word Processing, Spreadsheets, and PowerPoint.
Document Verification (DV):
- For all candidates who clear previous tiers.
- Involves checking educational certificates, age proof, and other documents.
“Read about the SSC CGL exam 2025 in detail- Click Here“
SSC CGL Syllabus 2025- TIER 1

Tier 1 exam consists of 4 sections each of 25 marks conducted for a duration of 1 hour. The sections include- Mathematics, logical reasoning, general knowledge and English. Let’s discuss about the detailed section wise syllabus for SSC CGL tier 1 exams:
Mathematics Syllabus
The Quantitative Aptitude syllabus for Tier 1 Exam mainly includes Number System, Arithmetic, Algebra, Geometry, Trigonometry, and Data Interpretation. Check sub topics below:
| Section | Topic |
| Number System & Arithmetic | Whole Numbers |
| Decimals | |
| Fractions | |
| Relationships Between Numbers | |
| Percentage | |
| Ratio & Proportion | |
| Square Roots | |
| Averages | |
| Interest (Simple and Compound) | |
| Profit and Loss | |
| Discount | |
| Partnership Business | |
| Mixture and Alligation | |
| Time and Distance | |
| Time and Work | |
| Algebra | Basic Algebraic Identities of School Algebra |
| Elementary Surds | |
| Graphs of Linear Equations | |
| Geometry | Triangle and Its Various Kinds of Centres |
| Congruence and Similarity of Triangles | |
| Circle and Its Chords, Tangents | |
| Angles Subtended by Chords of a Circle | |
| Common Tangents to Two or More Circles | |
| Triangle, Quadrilaterals, Regular Polygons | |
| Circle, Right Prism, Right Circular Cone | |
| Right Circular Cylinder, Sphere, Hemispheres | |
| Rectangular Parallelepiped | |
| Regular Right Pyramid with Triangular or Square Base | |
| Trigonometry | Trigonometric Ratios |
| Degree and Radian Measures | |
| Standard Identities | |
| Complementary Angles | |
| Heights and Distances | |
| Data Interpretation | Histogram |
| Frequency Polygon | |
| Bar Diagram | |
| Pie Chart |
“Finding it difficult to concentrate? Read about the techniques to find motivation to study.”
General Intelligence and Reasoning Syllabus
This subject tests general reasoning, application and intelligence of the students. The syllabus for this includes verbal and non verbal reasoning and the sub topics are as follows:
| Section | Topic |
| Analogy | Semantic Analogy |
| Symbolic/Number Analogy | |
| Figural Analogy | |
| Classification | Semantic Classification |
| Symbolic/Number Classification | |
| Figural Classification | |
| Series | Semantic Series |
| Number Series | |
| Figural Series | |
| Reasoning & Problem Solving | Problem Solving |
| Decision Making | |
| Judgment | |
| Analysis | |
| Syllogistic Reasoning | |
| Statement and Conclusion | |
| Drawing Inferences | |
| Coding-Decoding | Coding and Decoding |
| Small & Capital Letters/Numbers – Coding, Decoding and Classification | |
| Mathematical & Symbolic Operations | Arithmetical Reasoning |
| Numerical Operations | |
| Symbolic Operations | |
| Trends | |
| Visualization & Orientation | Space Visualization |
| Space Orientation | |
| Visual Memory | |
| Observation | |
| Discrimination | |
| Venn Diagrams | Venn Diagram based Questions |
| Classification of Centre Codes/Roll Numbers | |
| Folding & Patterns | Punched Hole/Pattern – Folding & Unfolding |
| Figural Pattern – Folding and Completion | |
| Embedded Figures | |
| Matching Concepts | Indexing |
| Address Matching | |
| Date & City Matching | |
| Word Building | |
| Other Concepts | Critical Thinking |
| Emotional Intelligence | |
| Social Intelligence | |
| Relationship Concepts |
English Language Syllabus
This test is conducted to test English language understanding and basic ability to comprehend and interpret the language. You do not have to be expert in English, basic fluency is needed to score well in this section.
| Topic | Definition |
| Reading Comprehension | Understanding and answering questions based on a given passage. |
| Synonyms-Antonyms | Identifying words with the same or opposite meanings. |
| Active Passive | Changing sentences from active to passive voice and vice versa. |
| Sentence Rearrangement | Arranging jumbled sentences to form a meaningful paragraph. |
| Idioms and Phrases | Understanding the meaning of common expressions. |
| One Word Substitution | Replacing a phrase with a single word. |
| Sentence Correction | Correcting grammatical errors in a sentence. |
| Error Spotting | Identifying mistakes in grammar, spelling, or usage. |
| Fill in the Blanks | Completing sentences by filling in the missing words. |
| Spellings Correction | Identifying and correcting wrongly spelled words. |
| Sentence Improvement | Improving sentence structure and grammar. |
| Cloze Test | Filling in blanks in a passage to complete the meaning. |
General Awareness Syllabus
General awareness paper tests the students’ understanding and knowledge about the surrounding, events and current news.
| Topic | Definition |
| Current Affairs | Latest events and happenings of national and international importance. |
| Important Days | Knowledge of significant national and international days and dates. |
| General Awareness of Environment Around and its Application to Society | Understanding of environmental issues and how they affect society. |
| Important Schemes | Key government schemes and programs for public welfare. |
| India and its neighboring countries especially pertaining to History, Culture, Geography, Economic Scene, General Policy & Scientific Research | Awareness of India’s and its neighbors’ historical, cultural, geographical, economic, political, and scientific aspects. |
| People in News | Notable personalities recently in the news for various reasons. |
| Portfolio | Current ministers and their respective ministries in the government. |
| Science | Basic scientific concepts and recent developments. |
| Books and Authors | Famous books and their authors. |
| Sports | Important sports events, players, and achievements. |
| Static GK | Fixed general knowledge facts, like capitals, currencies, national symbols, etc. |
SSC CGL Tier 2 Exam Pattern 2025
There are two papers in Tier 2 Exam: Paper 1 and Paper 2. Paper 1 is compulsory for all Posts whereas Paper 2 is only for Junior Statistical Officer post. Check details of both papers in the table below.

| SSC CGL Tier 2 Paper 1 Pattern | |
| Feature | Details |
| Exam Name | SSC CGL Tier 2 – Paper 1 |
| Total Sessions | 2 |
| Sections | 3 Sections (with modules) |
| Total Questions | 150 Questions + 1 Data Entry Task |
| Total Marks | 450 Mark |
| Total Duration | 2 hours 30 minutes |
| Mode of Exam | Online (Computer-Based Test) |
| Paper Type | Objective Type (MCQs) |
| Negative Marking | Yes (1 mark for each wrong answer) |
“Read about Updated UPSC Syllabus 2025“
| SSC CGL Tier 2 Paper 2 Pattern (For JSO Post Only) | |
| Feature | Details |
| Paper Name | SSC CGL Tier 2 – Paper 2 |
| Applicable For | Junior Statistical Officer (JSO) Posts Only |
| Subject | Statistics |
| Questions | 100 |
| Maximum Marks | 200 |
| Duration | 2 Hours |
| Mode of Exam | Online |
| Negative Marking | 0.50 |
SSC CGL Tier 2 Syllabus 2025
The SSC CGL Tier-II exam is conducted online with two papers:
Mathematical Abilities
| Part Name | Topic Name | Subtopics/Details |
| Paper 1: Section 1: Part A | Number Systems |
|
| Fundamental Arithmetical Operations |
|
|
| Algebra |
|
|
| Geometry |
|
|
| Mensuration |
|
|
| Trigonometry |
|
|
| Statistics & Probability |
|
Reasoning and General Intelligence Syllabus
| Part Name | Topic Name | Sub Topics |
| Paper 1: Section 1: Part B | Reasoning (Verbal & Non-Verbal) | – Semantic Analogy
– Symbolic/Number Analogy – Figural Analogy – Semantic/Number/Figural Classification – Semantic Series – Number Series – Figural Series – Problem Solving – Word Building – Coding-Decoding – Numerical Operations – Symbolic Operations – Trends – Space Orientation – Space Visualization – Venn Diagrams – Drawing Inferences – Punched Hole/Figure Folding & Unfolding – Figural Completion – Indexing – Address & Date Matching – Classification of Roll Numbers – Small/Capital Letter Coding & Classification – Embedded Figures – Critical Thinking – Emotional Intelligence – Social Intelligence |
English Language and Comprehension Syllabus
| Part Name | Topic Name | Subtopics |
| Paper 1: Section II: Part A | English Language | – Vocabulary
– Grammar – Sentence Structure – Synonyms/Antonyms & Usage – Spot the Error – Fill in the Blanks – Homonyms – Spelling Errors – Idioms & Phrases – One Word Substitution – Sentence Improvement – Active/Passive Voice – Direct/Indirect Speech – Sentence Reordering – Cloze Test – Reading Comprehension (3+ Passages on literature & current affairs) |
General Awareness Syllabus
| Part Name | Topic Name | Subtopics |
| Paper 1: Section II: Part B | General Awareness | – India & Neighboring Countries
– History – Culture – Geography – Economic Scene – General Policy – Scientific Research – Current Events – Daily Observations & Practical Knowledge |
Computer Knowledge and Proficiency Syllabus
| Part Name | Topic Name | Subtopics |
| Paper 1: Section 3 | Computer Basics | – Computer Organization
– CPU, I/O Devices – Memory & Storage – Backup Devices – Ports – Windows Explorer – Keyboard Shortcuts |
| Software | – Windows OS Basics
– Microsoft Word, Excel, PowerPoint |
|
| Internet & Email Usage | – Web Browsing & Searching
– File Downloading/Uploading – Email Account Management – e-Banking Basics |
|
| Networking & Cyber Security | – Network Devices & Protocols
– Information Security Threats (Viruses, Worms, Trojan, etc.) – Prevention Measures |
Paper 2 Statistics Syllabus (For JSO Post Only)
This paper is statistics and basic economics based and is conducted for JSO post only, those who have applied for Junior Statistical Officer position whose minimum qualification is having studied maths in 10+2 level.
| Subjects | Topics |
| Collection, Classification and Presentation of Statistical Data |
|
| Measures of Central Tendency |
|
| Measures of Dispersion- Common measures of Dispersion |
|
| Moments, Skewness and Kurtosis |
|
| Correlation and Regression |
|
| Probability Theory |
|
| Random Variable and Probability Distributions |
|
| Sampling Theory |
|
| Statistical Inference |
|
| Analysis of Variance | Analysis of one-way classified data and two-way classified data |
| Time Series Analysis |
|
| Index Numbers |
|
Conclusion
Knowing the syllabus is essential and the most crucial towards success when you are preparing for competitive exams or government exams. This detailed guide has addressed all the sections from exam brief, paper pattern, SSC CGL syllabus 2025 and last date to apply. Understand the core syllabus and thoroughly prepare for each section with sufficient mock tests. With consistency, patience and determination, you can clear this exam. All the best aspirants!
FAQs
- Will SSC conduct CGL exam for 2025?
Yes, the SSC (Staff Selection Commission) will conduct the CGL (Combined Graduate Level) exam in 2025.
- Is the exam notification for SSC CGL 2025 released?
Yes, The notification for the SSC exam 2025 has been released on the official website on 9th June 2025. The last date to apply for the exam is 4th July 2025.
- What is the last date to apply for the SSC Cgl exam?
Last date to apply for SSC CGL exams is 4th July 2025.
- Is the SSC CGL syllabus different from SSC CHSL?
Yes, while the core syllabus remains the same and is conducted in the similar format, the syllabus for both the exams differ slightly.
- When are SSC CGL exam 2025?
SSC CGL exam 2025 will be conducted from 13th to 30th August in 2025.
The post SSC CGL Syllabus 2025: Check out updated preparation guide appeared first on Eduexa.
UPSC Syllabus 2025- Download the latest syllabus 20 Jun 2025, 2:36 am
Preparing for UPSC CSE in 2025? The first thing you are searching for is the updated UPSC syllabus in 2025. For the beginners, let me tell you, having a clear understanding of the syllabus is the first step towards success in the UPSC CSE exam. Be it a first time aspirant or an experienced repeater, every candidate has to stay updated with the latest guidelines and syllabus of the exam. This blog will cover the complete syllabus of for upsc including, upsc syllabus for prelims, upsc syllabus for mains along with providing cse upsc syllabus pdf in a downloadable format.
Overview of the UPSC CSE exam
Union Public Service Commission (UPSC) conducts Civil Services Exams for recruitment under different government offices like IAS, IPS, IFS and other positions. These exams are conducted in 3 phases:- Prelims, Mains and the Interview.
STAGE 1: Prelims: This stage consists of 2 objective type papers conducted for a duration of 2 hours each. The marks of this round are not calculated for final rankings.
STAGE 2: Mains: It is a written exam where 9 papers are taken including 2 qualifying exams and the rest 7 as ranking.
STAGE 3: Interview: This is the final stage of UPSC CSE exam and the maximum marks for interview is 275.
“Read the complete detail about the UPSC exam“
UPSC Syllabus for prelims

The prelims exam consists of 2 papers- Paper I and II. Paper I is a general studies paper which tests general knowledge of the students over subjects like history, geography, economics, polity, art, culture and science. This paper is cut off based and hence the results depend on the marks obtained by other students. Paper II is a CSAT paper which tests the common aptitude of the candidates is of qualifying nature i.e. you just need to secure 67 marks to pass this exam.
| UPSC CSE Syllabus for Prelims | |
| Paper I- General Studies Paper | ● Current events of national and international importance
● History of India and Indian National Movement ● Indian and World Geography- Physical, Social, Economic geography of India and the World. ● Indian Polity and Governance- Constitution, Political System, Panchayati Raj, Public Policy, Rights Issues ● Economic and Social Development- Sustainable Development, Poverty, Inclusion, Demographics, Social Sector Initiatives, etc. ● General issues on Environmental Ecology, Biodiversity and Climate Change- that do not require subject specialisation ● General Science |
| Paper II- Civil Service Aptitude Test (CSAT) | ● Comprehension
● Interpersonal skills including communication skills; ● Logical reasoning and analytical ability ● Decision-making and problem solving ● General mental ability ● Basic numeracy(numbers and their relations, orders of magnitude, etc.) (Class X level), ● Data interpretation (charts, graphs, tables, data sufficiency etc.- Class X level) |
“Click here to download the upsc syllabus pdf for prelims”
UPSC Syllabus for mains
The Civil Services Main written examination consists of nine papers, two of which are qualifying and the other seven of which are ranking. Each paper lasts for three hours. Qualifying papers are ordered according to marks, and the Commission selects a few candidates for an interview or a personality test.
All of the questions in the UPSC Mains exam are of the descriptive answer variety. It’s a gruelling and time-consuming phase, and the total marks in UPSC mains directly determine your final grades. Consequently, the UPSC exam results for the mains phase play a critical role in determining the final merit list.

| PAPERS | SYLLABUS |
| PAPER 1 ESSAY | In this paper, candidates have to write 2 essays on any given topic. The topic would be open-ended as there is no prescribed syllabus for essay paper. |
| PAPER 2 GENERAL STUDIES I | ● Indian culture will cover the salient aspects of Art Forms, literature and Architecture from ancient to modern times.
● Modern Indian history from about the middle of the eighteenth century until the present significant events, personalities, issues. ● The Freedom Struggle —its various stages and important contributors/contributions from different parts of the country. ● Post-independence consolidation and reorganisation within the country. ● History of the world will include events from the 18th century such as industrial revolution, world wars, redrawal of national boundaries, colonisation, decolonization, political philosophies like communism, capitalism, socialism etc.— their forms and effect on the society. ● Salient features of Indian Society, Diversity of India. ● Role of women and women’s organisation, population and associated issues, poverty and developmental issues, urbanisation, their problems and their remedies. ● Effects of globalization on Indian society. ● Social empowerment, communalism, regionalism & secularism. ● Salient features of the world’s physical geography. ● Distribution of key natural resources across the world (including South Asia and the Indian sub-continent); factors responsible for the location of primary, secondary, and tertiary sector industries in various parts of the world (including India). ● Important Geophysical phenomena such as earthquakes, Tsunami, Volcanic activity, cyclones. etc., geographical features and their location-changes in critical geographical features (including water-bodies and ice-caps) and in flora and fauna and the effects of such changes. |
| PAPER 3 GENERAL STUDIES II | ● Constitution of India —historical underpinnings, evolution, features, amendments, significant provisions and basic structure.
● Functions and responsibilities of the Union and the States, issues and challenges pertaining to the federal structure, devolution of powers and finances up to local levels and challenges therein. ● Separation of powers between various organs dispute redressal mechanisms and institutions. ● Comparison of the Indian constitutional scheme with that of other countries. ● Parliament and State legislatures—structure, functioning, conduct of business, powers & privileges and issues arising out of these. ● Structure, organisation and functioning of the Executive and the Judiciary—Ministries and Departments of the Government; pressure groups and formal/informal associations and their role in the Polity. ● Salient features of the Representation of People’s Act. ● Appointment to various Constitutional posts, powers, functions and responsibilities of various Constitutional Bodies. ● Statutory, regulatory and various quasi-judicial bodies. ● Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation. ● Development processes and the development industry —the role of NGOs, SHGs, various groups and associations, donors, charities, institutional and other stakeholders. ● Welfare schemes for vulnerable sections of the population by the Centre and States and the performance of these schemes; mechanisms, laws, institutions and Bodies constituted for the protection and betterment of these vulnerable sections. ● Issues relating to development and management of Social Sector/Services relating to Health, Education, Human Resources. ● Issues relating to poverty and hunger. ● Important aspects of governance, transparency and accountability, e-governance applications, models, successes, limitations, and potential; citizens charters, transparency & accountability and institutional and other measures. ● Role of civil services in a democracy. ● India and its neighbourhood- relations. ● Bilateral, regional and global groupings and agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests. ● Effect of policies and politics of developed and developing countries on India’s interests, Indian diaspora. ● Important International institutions, agencies and fora- their structure, mandate. |
| PAPER 4 GENERAL STUDIES III | ● Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilisation, of resources, growth, development and employment.
● Inclusive growth and issues arising from it. ● Government Budgeting. ● Major crops-cropping patterns in various parts of the country,– different types of irrigation and irrigation systems storage, transport and marketing of agricultural produce and issues and related constraints; e-technology in the aid of farmers. ● Issues related to direct and indirect farm subsidies and minimum support prices; Public Distribution System- objectives, functioning, limitations, revamping; issues of buffer stocks and food security; Technology missions; economics of animal-rearing. ● Food processing and related industries in India- scope and significance, location, upstream and downstream requirements, supply chain management. ● Land reforms in India. ● Effects of liberalisation on the economy, changes in industrial policy and their effects on industrial growth. ● Infrastructure: Energy, Ports, Roads, Airports, Railways etc. ● Investment models. ● Science and Technology- developments and their applications and effects in everyday life. ● Achievements of Indians in science & technology; indigenization of technology and developing new technology. ● Awareness in the fields of IT, Space, Computers, robotics, nano-technology, bio-technology and issues relating to intellectual property rights. ● Conservation, environmental pollution and degradation, environmental impact assessment. ● Disaster and disaster management. ● Linkages between development and spread of extremism. ● Role of external state and non-state actors in creating challenges to internal security. ● Challenges to internal security through communication networks, role of media and social networking sites in internal security challenges, basics of cyber security; money-laundering and its prevention. ● Security challenges and their management in border areas– linkages of organized crime with terrorism. ● Various Security forces and agencies and their mandate. |
| PAPER 5 GENERAL STUDIES IV | ● Ethics and Human Interface: Essence, determinants and consequences of Ethics in-human actions; dimensions of ethics; ethics– in private and public relationships. Human Values lessons from the lives and teachings of great leaders, reformers and administrators; role of family society and educational institutions in inculcating values.
● Attitude: content, structure, function; its influence and relation with thought and behaviour; moral and political attitudes; social influence and persuasion. ● Aptitude and foundational values for Civil Service, integrity, impartiality and non-partisanship, objectivity, dedication to public service, empathy, tolerance and compassion towards the weaker sections. ● Emotional intelligence-concepts, and their utilities and application in administration and governance. ● Contributions of moral thinkers and philosophers from India and the world. ● Public/Civil service values and Ethics in Public administration: Status and problems; ethical concerns and dilemmas in government and private institutions; laws, rules, regulations and conscience as sources of ethical guidance; accountability and ethical governance; strengthening of ethical and moral values in governance; ethical issues in international relations and funding; corporate governance. ● Probity in Governance: Concept of public service; Philosophical basis of governance and probity; Information sharing and transparency in government, Right to Information, Codes of Ethics, Codes of Conduct, Citizen’s Charters, Work culture, Quality of service delivery, Utilisation of public funds, challenges of corruption. ● Case Studies on the above issues |
| PAPER 6- Optional paper 1 | Two papers are conducted for optional subjects. You choose 1 subject from song the following discourses:-
Agriculture Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Science Anthropology Botany Chemistry Civil Engineering Commerce and Accountancy Economics Electrical Engineering Geography Geology History Law Management Mathematics Mechanical Engineering Medical Science Philosophy Physics Political Science and International Relations Psychology Public Administration Sociology Statistics Zoology Literature of any one of the following languages: Assamese, Bengali, Bodo, Dogri, Gujarati, Hindi, Kannada, Kashmiri, Konkani, Maithili, Malayalam, Manipuri, Marathi, Nepali, Oriya, Punjabi, Sanskrit, Santali, Sindhi, Tamil, Telugu, Urdu, and English. |
| PAPER 7- Optional paper 2 |
Click here to download the UPSC syllabus pdf for Mains
Conclusion
Understanding the latest upsc syllabus and exam guidelines is an important step towards your success. Syllabus helps the students to analyze the topics they have to study so that they do not miss out on any topic. Prepare well for the exam and work hard to crack the exam in one go.
All the best aspirants! Stay focussed and stay updated!
FAQs
- Can I crack UPSC in 1 year?
Yes, with good understanding of upsc syllabus, strong will power, consistent efforts and self-belief can help you crack UPSC in 1 year.
- Is 60% required for Upsc?
There is no minimum percentage requirement for UPSC. You must have a minimum qualification of bachelors degree in order to be eligible for UPSC exams.
- Does Upsc revise its syllabus every year?
No, it does not always revise the syllabus but it is always recommended to check for the updated syllabus and guidelines.
- Does 12th marks matter in UPSC?
No, 12th marks does not matter in upsc. All the candidates who have cleared their graduation exams are equally eligible for UPSC exam.
The post UPSC Syllabus 2025- Download the latest syllabus appeared first on Eduexa.
Operation Rising Lion: Understanding Iran-Israel Conflict 18 Jun 2025, 2:34 pm
Recent News
On 13th June 2025, Israel launched Operation Rising Lion on Iran which dismantled Iran from within affecting major nuclear facilities and gas fields. This has grabbed global attention due to it being a major direct strike on the nuclear bases of Iran and it is likely going to shift the power and geo-political dynamics in the Middle East.
Overview of the Operation Rising Lion
| Attribute | Details |
| Name of Operation | Operation Rising Lion |
| Initiator | Israel Defense Forces (IDF) |
| Target | Iran’s nuclear infrastructure, ballistic missile factories, military capabilities |
| Key Hit Location | Natanz uranium enrichment facility, Isfahan Province |
“Preparing for UPSC Exams? Know about the Top 5 UPSC coaching in Delhi“
What is Operation Rising Lion? Where does the name come from?

It is a large-scale airstrike or jet strike campaign launched on Iran by the Israeli military. This operation is a planned escalation and affected Iranian bases due to Iran’s miscalculation. Operation Rising Lion is a major strike campaign that has directly targeted critical nuclear bases and facilities in Iran.
According to the report, Israel has named its military operation against Iran “Rising Lion” as it took the name from a biblical verse that vows for a victorious future for a powerful Israel.
Reasons that led to Operation Rising Lion
Immediate Trigger
Operation rising lion was launched as an immediate response to IAEA’s Non-Compliance Resolution. On 12th of June, IAEA passed a resolution stating Iran has violated its nuclear safeguard agreements and it is engaged in strengthening its nuclear power. Israel used this resolution as a green flag for launching its action on Iran.
Historical Context
Tensions between Iran and Israel is not a new thing. Shadow War and nuclear tensions were visible from early 1990s. The historical conflicts have sparked the current campaign.
Prevent Iran from strengthening its nuclear power
Iran has enriched its uranium sources to approximately 60% purity which is close to the weapon grade of 90%. Further Iran-Us talks failed because Iran reaffirmed on enriching the uranium.
Existential Threat
Iran’s better geo-political position and uranium enrichment supporting its nuclear armed status is considered an existential threat to Israel. Iran earlier maintained its stance of complete disappearance of Israel. And hence, Iran’s empowerment was the biggest threat to Israel.
Exploit Iran’s weakened global position
Iran’s allies i.e. Hamas, Hezbollah, and Houthis were weakened after Israel’s Gaza war (2023–25) and Syria’s regime collapse (2024). This weakened position of Iran was thereof a green flag for Israel’s well planned and strategically executed operation.
Domestic Political Needs
This operation was not just a country’s requirement but the domestic politics of Netanyahu for his own survival. Facing corruption charges and coalition instability, he framed the attack as critical for Israel’s security.
Why could Israel strike Iran’s nuclear bases?
While what might seem a sudden strike was a planned and strategically executed move by the Israeli defence force. Israel military could strike Iran’s nuclear bases and successfully launch operation rising lion due to following reasons:-
- Planned Strategy: Israeli media and news channels created a fake narration to make Iran believe that Netanyahu is busy with personal stuff.
- Iran’s miscalculation: Iran ignored all the signs that prompted possible action by Israel assuming peace for the nation.
- Previous victory: Previously, Israel neutralised Iran’s attack easily. And a prolonged surge has also weakened its allies.
- Green flag from IAEA: IAEA’s recent accusation on Iran’s nuclear safeguard acted as a green flag for Israel.
Iran’s Nuclear Sites in the News:
- Natanz Nuclear Facility (Isfahan Province):
-
-
- This site is Iran’s primary uranium enrichment centre, referred to as the “beating heart” of its nuclear programme. This was the major site targeted by Israel under operation rising lion.
- Severely damaged in Israel’s strike, including major surface infrastructure.
-
- Fordow Enrichment Plant (Qom Province):
-
-
- It is a plant located deep underground and is highly critical for high-grade enrichment.
- Site reported explosions suggest it was partially targeted in follow-up strikes.
-
- Bid Kaneh Missile Complex:
-
-
- A key site for missile development and production.
- Hit by precision strikes targeting strategic deterrence capability.
-
- Kermanshah Missile Base:
-
- Central hub for short and medium-range missile storage.
- Hit to restrict Iran’s retaliation capabilities.
- Tabriz Military Bases & Research Centre: Targeted to cripple military command structures and destroy ballistic storage units.
- Tehran Command Centre: Underground base where Iran’s IRGC air force leadership was meeting key commanders killed.
Implications of the Iran-Israel Conflict

Every action has a reaction and so does “Operation Rising Lion”. The possible expected implication of this Iran-Israel Conflict are discussed below:-
- Escalation of Proxy Conflicts: Iran’s regional proxies — Hamas, Hezbollah, Houthis, and PMF — may retaliate, opening multiple fronts and turning the war into a wider Middle Eastern conflict.
- Destabilization of Fragile States: Countries like Lebanon, Iraq, Syria, and Yemen could witness a surge in violence, leading to internal political chaos and humanitarian crises.
- Change in regional dynamics: This operation is likely shifting the geo-political stance of the region and other dynamics.
- Surge in Oil Price: Iran is a major oil producing state and a direct war involving Iran risks disrupting global oil exports, potentially triggering a spike in oil prices and inflation worldwide.
- Maritime Insecurity: Attacks over the red sea in 2024 makes us believe that maritime security can be at risk. Key shipping routes like the Strait of Hormuz, Bab el-Mandeb, and Eastern Mediterranean may face threats, disrupting global trade and energy supply.
- Derailment of Iran Nuclear Deal Talks: Ongoing efforts to revive the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA) are likely to collapse, ending hopes for a peaceful nuclear settlement.
- Strengthening Iran’s Resolve: Israeli strikes on nuclear facilities may encourage Iran to accelerate its nuclear weapons program under the pretext of national defense.
- Arms Race in the Region: Gulf countries like Saudi Arabia may push for nuclear capabilities, intensifying the regional arms race.
- Reconfiguration of Regional Alliances: Arab states fearful of Iranian aggression may deepen cooperation with Israel.
- Regional powers like Turkey may recalibrate their roles to balance influence, while Russia may attempt to exploit the crisis for strategic gains.
- India’s Strategic and Economic Concerns: Over 60% of India’s crude oil comes from the Middle East; instability can disrupt supplies and widen the current account deficit.
- Millions of Indian citizens work in the Gulf; escalation may require emergency evacuations and increase remittance risk.
- India will have to balance relations between Israel, Iran, and Arab countries, maintaining neutrality while protecting its strategic interests.
“Read about India’s Neighbourhood First Policy“
FAQs
- What exactly did Israel target in Iran?
Israel’s strikes focused on nuclear facilities, missile production sites, and senior Iranian military figures, according to reports.
- Who are involved in the operation rising lion?
Israel and Iran are involved in the operation rising lion.
- What is the recent Iran-Israel conflict?
Israel has launched Operation Rising Lion striking the nuclear facilities, missile production sites, and senior Iranian military figures.
- Why is it called Operation Rising Lion?
Because the name is taken from a Bible verse, which symbolizing Israel’s strength and determination, comparing the nation to a lion rising for battle, as per Reuters report.
The post Operation Rising Lion: Understanding Iran-Israel Conflict appeared first on Eduexa.
Bonafide Certificate Format, Uses and Application 17 Jun 2025, 2:30 am
Applying for scholarships or perhaps for a loan, you might have come across the word “Bonafide Certificate”. It is a crucial official document but do you know what it actually means and what are its uses? If your answer is No, don’t worry this blog will discuss about the bonafide certificate format, its uses and application letter.
What is a Bonafide Certificate?
The term “bonafide” originates from Latin, meaning “in good faith.” A bonafide certificate is a crucial official document which acts as a proof of your enrollment in a particular institution. This document is issued by your educational institution or organization to validate that you belong to that institution. Whether you’re a student applying for scholarships or an employee applying for a loan, this certificate acts as proof of association or credibility.
Key Features of a Bonafide Certificate
Let’s quickly understand some of the key features of bonafide certificate format
- It is issued by an educational or professional institution.
- The certificate contains the institution’s letterhead and seal.
- Also confirms the duration and nature of association.
- Often required for official or government processes.
Uses of a Bonafide Certificate
While you come across this term a lot, what are its uses? Is it just for the students? Bonafide certificates serve various purposes for both students and employees. Below are the most common use cases:
For Students
- Scholarship Applications – Major use of bonafide certificates is for scholarship applications. It acts as a proof to confirm that you are currently enrolled in an institution.
- Education Loans – Student loans are commonly needed for studying in top institutions like IIMs, IITs as well as for studying abroad. Financial institutions often ask for documents like the bonafide certificate to verify your student status.
- Visa Applications – Your studying abroad decision often comes with complex processes and document curation. One such document is a bonafide certificate required at the time of visa application.
- Public Transport Concessions – Want to get a bus pass? You will require this document to avail student discounts on buses, trains, or metros.
- Internships & Job Applications – Internships and job applications also need a verification proof or authentic document to verify your association from a recognised institution.
- Opening a Student Bank Account – Make sure you have a valid association proof in order to open a student account in any bank.
For Employees
- Loan Applications – Employment status confirmation is necessary when you are applying for a loan.
- Visa Processing – Helps during work visa applications like H1B visa etc. as proof of employment.
- Professional Certifications – Some certifications require employment verification.
- Government Documentation – For various formalities like passport issuance, etc.
“Do you know the full form , uses and calculation method for CGPA? Click here to learn”
Bonafide Certificate Format
The format of a bonafide certificate may vary depending on the issuing authority, but a standard bonafide certificate includes the following elements:
| Essential Elements | |
| Institution’s name and address | Certificate reference number (if any) |
| Date of issue | Name of the student/employee |
| Course or position held | Duration of association |
| Purpose for which the certificate is issued | Signature of the head of the institution or HR department |
| Official stamp or seal of the institution | |
“Finding it difficult to stay motivated? Learn about the top strategies to find motivation to study“
Sample Bonafide Certificate Format (For Students)

[Institution Letterhead]
[Delhi University]
[South Campus, Delhi, 112001]
[151-xxxxx/ delhiuniveristy@gmail.com]
Date: 17/06/2025
TO WHOMSOEVER IT MAY CONCERN
This is to certify that Ms. Riya Jain, daughter of JK Jain , is a bonafide student of Delhi University, currently enrolled in Bsc Applied Science from 10/06/2025 to 30/05/2028.
This certificate is issued upon the request of the student for the purpose of [e.g., applying for an education loan/scholarship].
Seal & Signature
(Principal/Head of Department)
[Institution Seal]
Sample Bonafide Certificate Format (For Employees)
Bonafide certificate format for employees is slightly different from the student’s certificate. The format is as follows:-
Here is the sample bonafide certificate format for employees:-
[Company Letterhead]
[Company Name]
[Address]
[Phone Number/Email]
Date: DD/MM/YYYY
TO WHOMSOEVER IT MAY CONCERN
This is to certify that Mr./Ms. [Employee Name] is a bonafide employee of [Company Name], working as a [Designation] in the [Department] since [Date of Joining].
This certificate is being issued for the purpose of [e.g., applying for a personal loan/work visa].
Seal & Signature
(HR Manager/Authorized Signatory)
[Company Seal]
How to Apply for a Bonafide Certificate
After knowing the bonafide certificate format, here comes the most important question: “How to Apply for a bonafide certificate”? Most of the students and even employees do not know the process. Applying for a bonafide certificate is usually a straightforward process. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
For Students:
STEP 1: Visit the Administration Office – Go to the registrar or student enquiry department of your college or university with all the necessary official documents. You can also enquire online before actually visiting the office so that you do not miss out on any important document.
STEP 2: Submit a Written Application – You have to submit a written application that includes your name, course details, enrollment number and purpose of bonafide certificate.
STEP 3: Attach Supporting Documents – Just submitting the application alone is not enough, you need to attach other documents like ID proof, admission receipt, etc.
STEP 4: Pay Nominal Fees (if required) – Some institutions charge a processing fee. You have to check through your college’s official site or you can enquire at the administrative office if any fee is charged.
Reminder: Collect the Certificate – Usually issued within 2–5 working days.
Sample Application for Bonafide Certificate (Students)
To
The Principal
[Institution Name]
[Institution Address]
Subject: Request for Bonafide Certificate
Respected Sir/Madam,
I am [Your Name], a student of [Course Name], Roll No. [Roll Number], currently studying in [Year/Semester]. I require a bonafide certificate for the purpose of [e.g., applying for a student visa].
Kindly issue the certificate at your earliest convenience.
Thanking you.
Sincerely,
[Your Name]
[Contact Details]
For Employees:
STEP 1: Contact HR Department – You can make a request through email or in person.
STEP 2: State the Purpose – Mention why you need the certificate.
STEP 3: Mention Details – Include designation, employee ID, and department.
STEP 4: Wait for Processing – Usually takes 2–3 days depending on company policy.
Sample Email Request for Bonafide Certificate (Employees)
Subject: Request for Bonafide Certificate0
Dear [HR Manager’s Name],
I am writing to request a bonafide certificate stating my employment with [Company Name] as a [Designation]. The certificate is required for [mention purpose, e.g., applying for a home loan].
Kindly let me know if any further details or documents are needed from my end.
Thank you for your assistance.
Best regards,
[Your Full Name]
[Employee ID]
[Department]
Important Points to Remember
While the process of applying and using bonafide certificate is simple and without any complexion, it is important to remember following few things when you are applying for it:-
- Enquire about the application process and fees in advance with your institution so that you are well prepared for all the formalities in advance.
- Be ready with your application letter and clearly mention the purpose of the certificate.
- Verify and reverify the correct spelling of names and details before submission.
- Keep both digital and hard copies for future reference.
- Apply in advance as it may take time to be processed.
“Planning to study abroad? Read about the IELTS exam syllabus and preparation tips”
Conclusion
To sum up, we have discussed complete details about bonafide certificate including meaning, sample and bonafide certificate format. A bonafide certificate is more than just a piece of paper—it’s a verified document that validates your identity as a student or employee of an institution. Whether you are applying for a visa, loan, or scholarship, having a bonafide certificate can simplify many formal procedures. Always ensure you provide accurate details and follow the correct process to avoid any delays or rejections.
Faqs
- How can I apply for a bonafide certificate?
As a student you have to visit the administrative office and for employees, you can contact your HR.
- Who needs a bonafide certificate?
Any one applying for scholarship, loan or for any government purpose can require bonafide certificate.
- What is the full meaning of bonafide?
It is a latin word meaning “in good faith”.
- What is the use of bonafide?
A Bonafide certificate is used for many official and government purposes. It is a document used as proof of association with any institution or organisation. It might be needed at the time of loan application, scholarships, visa requirements, or other official purposes.
The post Bonafide Certificate Format, Uses and Application appeared first on Eduexa.
GPA Full Form: 2025 Updates for Students 16 Jun 2025, 1:38 am
Hi Future Leaders, Scholars and Innovators! Now, let’s visit the three-letter acronym that likely crosses your brain like a swatted mosquito more often than you’d like: GPA. For students in India, the Grade Point Average or GPA full form seems odd, if not potentially disturbing at times; as our education system calculates scores more often than not as a percentage or CGPA. However, as the world continues to place value on GPA, as students in India – that’s extremely important for you, especially if you are considering study abroad opportunities, potential top scholars, or chasing internship goals.
But the beauty of it is this: understanding GPA and its changing role, along with effectively approaching it is much less complicated than you probably think. This is about so much more than a number! This is about changing your course of study into a language everyone understands, and getting the most out of your journey and process!
In this conclusive document, we are going to break down the essential details and updates to how GPA period for students from India in 2025 (and beyond). We are going to help you understand GPA full form, how to demystify GPA calculation, and assess what it actually means for your future; as well as provide strategies to make progress towards your goals!
Why All the Fuss About GPA?

For decades, the Indian academic environment was based on percentage scores. So why the sudden shift toward GPA? The answer is globalization. With many Indian students wanting to study at international universities and multinational corporations looking at young Indian talent, a standardized academic metric, such as GPA, becomes clear.
You can think of GPA as a universal academic currency that allows institutions and employers around the world to quickly assess your academic standing regardless of the different grading systems in different countries.
Yet, it’s not just international applications. Here is where the GPA sticks out:
– International University Admissions: This is probably the biggest reason why students care about GPA. Universities in the US, Canada, the UK, and many European countries almost always use the GPA on a 4.0 or 5.0 scale when considering students for admissions. Converted GPAs are often the first of which admissions committees consider when reviewing applications.
– Scholarships and Financial Aid: Merit scholarships and need-based financial aid all have increasingly specific GPA requirements. A solid GPA (usually 3.0 or 3.5 and above) will often be a primary exclusionary state of eligibility. In fact, many more competitive scholarship opportunities specifically list GPA cut-off requirements for Indian students wishing to study abroad.
– Internships and campus placements: Yes, even in India! Many employers (especially those offering international placements or highly competitive positions) are particularly screening for GPAs when filtering applications for campus placements, and even internships. Employers are often looking for signals of consistency and quality of work, and GPAs are certainly related to them.
– Graduate/Post-Graduate Programs: For MBA, MS or PhD programs, your undergraduate GPA (or converted equivalent) will be a key or baser element to your application.
– Student Organizations and Honors: Obtaining a certain GPA breadth will often qualify you for transformative experiences within academies such as joining, academic clubs, honour societies, or even the Dean’s List, which will enhance your overall development portfolio.
“Want to pursue MBA from best college? Discover the tier 1 colleges for MBA“
GPA full form and meaning
Reading about the term GPA and still not aware about the full form? GPA full form is Grade point average. Grade point average is a simply a measuring index or a calculation scale which calculates the academic scores of the student by averaging all the grade points. This grade point reflects the academic success of the students and it measures the score across terms, semesters and years.
Demystifying GPA: Understanding the Different Scales & Calculations
GPA full form is Grade Point average. One of the biggest areas of confusion for Indian students is the number of different GPA scales. Let’s overview the main ones you will see, and most importantly how your Indian percentage or CGPA will convert.
- The 4.0 GPA Scale (most common worldwide): This is the standard GPA scale used in the United States and Canada. Your percentage or grade is converted to points based on a standard scoring where A = 4.0, B = 3.0, C = 2.0, D = 1.0 and F = 0.0. Many universities as well, will have pluses (+) and minuses (-) scoring of grades. An A would be a 4.0, an A- might be a 3.7, B+ = 3.3 etc.
- The 5.0 GPA Scale: Less common, but still used by some institutions, in particular for more advanced/honors programs. An A could potentially be a 5.0
- The 10.0 GPA/CGPA Scale (common in India): A lot of universities, particularly in India, will use a CGPA (Cumulative Grade Point Average) system with 10 points used. Your percentage will easily convert to CGPA, usually directly (… for instance an 85% could convert to an 8.5 CGPA).
Example on a 4.0 Scale:
| Subject | Grade | Grade Points | Credits | Grade Points × Credits |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Math | A | 4.0 | 3 | 12.0 |
| English | B | 3.0 | 3 | 9.0 |
| Science | A- | 3.7 | 4 | 14.8 |
GPA = Total Grade Points / Total Credits = (12 + 9 + 14.8) / 10 = 3.58
Weighted vs. Unweighted GPA: What’s the difference?
Unweighted GPA: This is a simple average of grades (in other words, all courses are treated equally, regardless of course difficulty); a 4.0 GPA is an unweighted perfect score on a 4.0 scale.
Weighted GPA: This account for difficulty and weights or “points” are assigned for difficult courses such as Honors, Advanced Placement (AP), International Baccalaureate (IB) or advanced university-level electives. For example, an A from an AP course may be assigned 5.0 points (instead of 4.0). Weighted GPA often results in a GPA above 4.0, and places a premium on those students who take advanced courses and challenge themselves academically.
Semester G.P.A. vs. Cumulative G.P.A. (CGPA)
Semester G.P.A. (SGPA): This is your G.P.A. based on a single academic term or semester. It is a snapshot of your academic performance for that particular term.
Cumulative G.P.A. (CGPA): This is your average of all your grades across your full academic program (e.g., your entire bachelor’s degree). This is what universities and employers will generally look at in terms of your academic background.
“Preparing for entrance exams? Read about the CUET-UG exam“
How to Convert Your Indian Percentage/CGPA to a 4.0 GPA (The Important Part!):
This is where we typically see the “recent updates” – not truly new formulas; just constant need for accurate conversions for overseas applications.
Simple Percentage to 4.0 GPA (Common Estimation): A very commonly accepted, albeit seldom more than a simple, formula is : GPA (on a 4.0 scale)=(Your Percentage÷100)×4 Example: If your score is 80% then GPA=(80÷100)×4=0.8×4=3.2
10.0 CGPA to 4.0 GPA: If you earned your university CGPA using a 10.0 scale a common and widely used way to convert is: GPA (on a 4.0 scale)=(Your CGPA÷10)×4 Example: If you’re CGPA is 8.5 then GPA=(8.5÷10)×4=0.85×4=3.4
GPA Calculator: Online GPA calculators are great for rapid and accurate conversions of your percentages/CGPA if you have credit hours for each subject. Many portals for study abroad offer them. Always cross-check with an universities preferred conversion method if they have a method available.
Professional Credential Assessment Services (WES): When applying to US/Canadian institutions you almost assuredly will always need to use a credential assessment service such as WES (World Education Services) as they will have their own proprietary way of calculating your Indian transcripts to an equivalent US GPA and often the evaluation is even mandatory. This is the most official “update” or process for international applicants.
Beyond the Numbers: The Big Picture with Your GPA in 2025
While GPA still matters, the latest trend in admissions and hiring is a shift from strict number to holistic review. This is good news because while you can get in the door with a solid GPA, a good GPA alone will not secure you get hired…
Admissions committees and hiring managers are increasingly also paying attention to:
- Course Rigor: Did you take classes that challenged you? A 3.5 achieved in tough courses often looks better than a 4.0 achieved in easy classes.
- Grades Trend: Did your grades improve over time? An improvement dipslayed over time, and especially growth, growth, growth is very appealing.
- Extracurriculars: What else did you do outside of academia? Leadership, volunteering, clubs and projects display well-roundedness.
- Essays & Personal Statements: What did you write about? Your unique story, motivation and goals can be a powerful way to capture your personality and drive.
- Letters of Recommendation: What is being said about you by your professors or a personal mentor around your character, work ethic and future potential?
- Standardized Test scores: Many universities have moved toward test-optional; however, a strong SAT, ACT, GRE, or GMAT score can be used to strengthen your application if needed.
So, while your percentage remains vital within India, understanding and optimizing your GPA is no longer optional – it’s a strategic advantage.
“Read about CGPA full form, meaning and uses in detail”
How to Increase your GPA: Helpful Tips for Every Student

Stressful? Don’t be! Whether you’re trying to keep your GPA up or make a dramatic increase, here are useful recommendations:
- Understand Your Syllabus & grading process: This may seem easy, but you have to understand every aspect of how each course will be graded (assignments, exams, participation weightings, etc.) so you know how to prioritize your time.
- Master Time Management: College is busy! Use planners, calendars, or an app to define your study time, assignments, and personal tasks. Being consistent is important.
- Attending Classes & Participating in Classes: Just being there isn’t enough. Make sure you’re engaged! Ask questions, participate in discussions, use that time productively. It will help you in the course, and some professors will include your participation as part of your grade.
- Talk to Your Professors: Do not hesitate to stop by during office hours. Professors can be great mentors for clearing up questions or misconceptions, recommending upgrades for future assignments, and can be valuable in discussing potential career paths. In some cases gaining familiarity could lead to a product that would be a stronger recommendation letter.
- Form Good Study Groups: Work with classmates who share the same mentality about school work as you. When you explain a concept to someone, or explore a set of problems together, you develop a better understanding of the subject.
- Address Tough Courses First: Make sure you spend extra time your studying for those courses you find difficult. Go after the work head-on. Don’t let difficult courses scare you off. Get help if you need it (by tutors, online sites).
- Review, Review, Review, Don’t Cram: Consider breaking down parts of your studying into smaller components. You will always retain more material this way than trying to cram all your studying last minute.
- Use Academic Resources: Most universities will have academic resources for free. This could be tutoring services, writing center, academic advising….use them, they are there to help you.
- Balance your workload: Don’t take 3 difficult courses in the same semester. Careful planning of where you might use your electives with core requirements will help you keep a reasonable GPA.
- Don’t forget you: You are important. Your mental health and physical health will directly affect your study of materials. Use your time wisely to exercise, eat well, and take care of stress. A burnt out student will not be able to achieve the potential they have.
“Learn about the upcoming government exams in 2025“
The Main Idea: Your GPA, Your Journey
The world of academic assessment is in perpetual flux, but GPA has unequivocally emerged as a considerable currency for students in India seeking possibilities overseas. Simply put, it is a measure of your academic commitment and capabilities.
That being said, keep in mind that GPA is a relatively big measure, but it is only part of who you are or will be in the larger scheme of things. It is a means of access, not the only means of access to the proverbial land of milk and honey. Your main focus should be the processes of working consistently, learning authentically, and building a complete profile that reflects who you are.
Once you have learned about GPA full form and its meaning, taken some steps to own your academic performance, and have done some planning to use the available resources, you will be in the position to enjoy your academic journey and embrace many meaningful opportunities ahead.
Are you ready to start calculating your current GPA or searching for some scholarships based on your academic history? If you have any questions from the blog, please add them in the comments or check out our suggested GPA calculator [Link to a relevant GPA calculator tool/resource if you have one].
FAQs
Q1: What is the full form of GPA?
A: GPA stands for Grade Point Average.
Q2: What is a good GPA?
A: A GPA of 3.5 or above (on a 4.0 scale) is considered good and competitive.
Q3: Can GPA be converted to percentage?
A: Yes, approximate conversion formulas exist. For example, in India:
Percentage = GPA × 9.5 (for 10-point scale in CBSE).
Q4: Does GPA matter after college?
A: For academic roles and early-career jobs, yes. Later, work experience becomes more important.
The post GPA Full Form: 2025 Updates for Students appeared first on Eduexa.
Impact of AI in Education: Transforming the Future of Learning 15 Jun 2025, 5:09 am
Introduction
AI in education is no longer a distant dream, it is a present day reality that is slowly transforming the education model and learning outcomes. With the incorporation of artificial intelligence, the education sector is undergoing digital transformation which has changed student’s learning and interest, teacher’s teaching pattern and overall academic results.
What is artificial intelligence?
Artificial Intelligence refers to programming human intelligence into machines. Simply speaking it refers to the ability of the machines or robots to perform the tasks which typically require human intelligence and understanding.
Artificial intelligence in education means use of Ai driven techniques and technologies in education and learning platforms to offer adaptive and personalized educational experiences to students. Ai facilitates in instruction, automated work and administration with ease and perfection.
Benefits of AI in education
Application of AI in education has truly transformed the academic and learning outcomes. The benefits of Artificial Intelligence are multifaceted which spreads across classes, courses and students. Some of the benefits are discussed below:-
Personalized learning
Customized shirts and gifts feel so personal and reliving. Now think of a customized learning model? The best application and outcome of artificial intelligence in education is the personalized learning model. Each student has its own profile on the AI tools and hence these tools use algorithms to devise personalized learning paths. These learning models are specifically based on a student’s strengths, weaknesses, learning behaviour and pace.
Real time feedback
Tareek pe Tareek is really daunting and especially when you are anxiously waiting for the test results. At earlier times, we used to wait for a minimum of 2-3 days for a normal 20 marks test results. And this delayed test score and feedback used to make students more anxious and less productive. Now with the integration of AI, computer based tests which can give quick results has made the journey smoother. Let’s take an example of a test series of competitive exams like testbook, adda247 which gives instant test feedback so students can work on their weaknesses early.
Global accessibility and inclusion
Artificial intelligence has made education accessible to all. Professors at top universities like Harvard, Ivy league and MITs are now teaching students in India. Students now do not have to shift to other destinations in order to access the top educational facilities and faculty teachings. With this facility, every student irrespective of his location can access education and it increases inclusivity.
Ease and Convenience
AI has not only given one stop solution and amenities but also transformed the educational landscape by providing ease and convenience to students as well as teachers. Teachers do not have to check the 100s of test copies manually instead they can use this time in taking student’s queries. Students now do not have to travel for hours to reach the test centres, they can take the mock exams online from their home reducing travel cost.
Better outcomes
Imagine I take you to a virtual tour of Indus Valley Civilization showing you the town planning, administrative units, seals and potteries. Now imagine I am explaining about civilization verbally. What do you think would interest you more? Obviously the virtual tour, because not only you will be interested in learning but you will also remember about this through the experience. Hence, with a proper learning model, students retain more and remember better leading to desired outcomes.
“Read about the upcoming government exams in 2025“
Challenges in implementing AI in education
The benefits of Artificial intelligence in education are numerous and undoubtedly it has left a transforming impact on the learning system and education outcomes. But each coin has two sides. These benefits come with a cost and it can pose some serious challenges to users at large. Some of the challenges are as follows:-
Right to privacy impacted
While we have the right to privacy as our fundamental right, developments like AI are possibly taking those rights away. These AI based tools use personal information and preference in order to generate personalised results. So, you have to give personal information as inputs.
Possible data breaches
AI systems collect vast amounts of data such as personal information, contacts, sometimes facial recognition, in addition to recording the behavioral patterns and habits. As such there are rising concerns about how this data is stored, used, and protected.
Cyber security challenges
Cyber security threats are no joke. One click and all your data is gone. Most of the people today are by themselves sharing their personal information to AI tools unaware of the cyber security challenges it might pose. Not all the apps are trustworthy and hence some of the tools might result in scams.
Algorithm based biases
It records the pattern and behaviour of the user and hence shows the outcome based on the user’s pattern. This saved algorithm may possibly show biased content skewed toward the student’s personal interests and likings.
High implementation costs
AI technology is truly transforming and this transformation needs huge costs. Implementing AI in schools, colleges and coachings require top-notch technologies, systems and softwares which costs a lot initially.
Resistance to change
Modern solutions are always challenged by the people’s mindset and resistance to change. People are more comfortable with the old methods and as such are not always willing to change or adapt to new technologies. Oldest faculties or traditional teachers find it difficult to operate the new AI driven classrooms and lectures.
Pre-assumed threat to jobs
Some people believe that AI will replace teachers in the future. As a result, teachers are unwilling to promote and use AI tutoring. Though that’s not true, AI is meant to ease the work of teachers and help students understand better.
Lack of 100% Reliance
These updated technologies are just gadgets after all. You can not rest assured about the results, any technical glitch or error can lead to flawed results.
“Do you know about the CGPA System? Lean everything about CGPA here”
AI and teachers: Possible impacts of AI in education
AI has assisted teachers in possibly every task be it delivering the lectures, conducting mock tests, curating videos and animation. Let us understand the tasks being taken up or assisted by AI:-
Automated tasks:- Ai assists in everyday tasks such as attendance, grading, assessments etc which take up much time of teachers.
Interactive Classes:- You can show the huge volcanic eruptions to small microscopic organisms all through smart classes. These interactive sessions and videos boosts student’s inquisitive sight and interest.
Performance Analytics:- Providing insights into student performance trends to help teachers adjust their teaching strategies.
Smart Content Creation: Teachers can generate Ppts, interactive quizzes, activity etc easily using Ai generators.
How has Ai in Education impacted students?
Personalised Learning Experiences: AI enables adaptive learning platforms that tailor content to each student’s pace, strengths, and weaknesses. For example- Vision IAS personalised test series based on your strengths and weaknesses.
Competitive resources and classes: Students can now look for competitive study materials of different coachings and faculties in literally no time.
24\7 Availability: AI has removed all the barriers in student’s learning. Not just geography, even time is no longer a constraint, you can access these AI based platforms at any time. Whether you are a night owl or an early bird, all you need is dedication to study, resources can be made available at any time.
Breaking language barriers: Real time translations and automated caption generation has assisted the students at large. It has breaked all the language barriers coming in the way of learning success.
Conclusion
The impact of Artificial intelligence in education is truly transformative and revolutionary. From personalized learning to streamlined administration, AI is reshaping the educational landscape. While there are challenges to overcome—such as data security and cost—its potential benefits far outweigh the drawbacks.
As we move towards a more digitized future, embracing AI in education is not just an option—it is a necessity for creating inclusive, efficient, and forward-thinking learning environments.
FAQs
Q1: What is the role of AI in education?
AI helps personalize learning, automate administrative tasks, and improve access to quality education.
Q2: Can AI replace teachers?
No. AI complements teachers by handling repetitive tasks, but it cannot replicate human mentorship and emotional intelligence.
Q3: What are the main benefits of using AI in education?
The main benefits include personalized learning, improved accessibility, administrative efficiency, and student performance tracking.
Q4: Are there risks involved with AI in education?
Yes, including data privacy concerns, algorithmic bias, and the digital divide.
The post Impact of AI in Education: Transforming the Future of Learning appeared first on Eduexa.
CGPA Full Form: Meaning, Importance, and Calculation in 2025 14 Jun 2025, 5:44 am
CGPA full form is Cumulative Grade Point Average, It is one of the important indicator of academic performance. to know about CGPA is very important, it’s uses, how CGPA calculated and how it is different from GPA and SGPA? Read this blog till the very end you will get to know everything related to CGPA.
What is an CGPA?
CGPA stands for Cumulative Grade Point Average. CGPA is a numerical representation of student’s academic performance during a period of time, for say a semester or a year. It is used in Indian Education system as well as Globally to make grading system as standardized. CGPA influence various aspects of student’s career from further education, scholarships to jobs CGPA have an important role to show student’s academic excellence.

Why is CGPA Important- Benefits of CGPA
CGPA plays an important role in student’s career as CGPA will help students in scholarships, further educational opportunities, jobs and much more. CGPA is one of the important indicator to show student’s academic excellence. Here are some other importance factors-
- Apply for college admissions
- Sit for competitive exams
- Secure scholarships
- Build a strong academic portfolio
- Apply to foreign universities
Benefits of CGPA
-
Simplified Evaluation: Converts multiple subject marks into one comprehensive score.
-
Consistency Across Systems: Allows comparability between students and schools.
-
Encourages Balanced Learning: Focuses on overall development, not just marks.
Limitations of CGPA
Despite it’s show much importance, CGPA have some limitations and challenges-
Lack of Detail:
CGPA may not offer a detailed breakdown of a student’s performance in specific subjects or areas of study. It just show the cumulative or total average which don’t provide a detailed overview for strong and weak subjects to students.
Contextual Differences:
The grading scale used for CGPA calculation may not consider contextual differences in education systems, leading to disparities in assessment.
Omitting Important Details:
Relying solely on CGPA may overlook important aspects of academic achievement, such as extracurricular activities or practical skills.
CGPA in Indian Education System (2025 Update)
According to CBSE guidelines, the CGPA system was introduced to reduce exam stress and focus on learning rather than rote memorization.
CBSE Grading Scale- Latest
| Grade | Grade Point |
|---|---|
| A1 | 10 |
| A2 | 9 |
| B1 | 8 |
| B2 | 7 |
| C1 | 6 |
| C2 | 5 |
| D | 4 |
| E1/E2 | Fail |
Formula to calculate CGPA:
CGPA = Sum of grade points in all subjects / Number of subjects
Example: If your subject-wise GPAs are 9, 8, 10, 9, and 8
Then, CGPA = (9+8+10+9+8) / 5 = 8.8
How to Convert CGPA to Percentage: Convert Your Grades Easily
Understanding the concept of converting CGPA to Percentage is important as some institutions and Employers consider percentange, so here is a simple calculation of convert CGPA to percentage-
According to the CBSE (Central Board of Secondary Education) guidelines and widely accepted academic standards in India, the formula to convert CGPA to percentage is:
Percentage (%) = CGPA × 9.5
Example: How to Convert CGPA to Percentage
Let’s say your CGPA is 8.2.
Using the formula:
Percentage = 8.2 × 9.5 = 77.9%
So your score is 77.9%.
| Grade | Grade Point (GP) | CGPA Range | Percentage (Approx) | Performance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | 10 | 9.1 – 10 | 91% – 100% | Outstanding |
| A2 | 9 | 8.1 – 9.0 | 81% – 90% | Excellent |
| B1 | 8 | 7.1 – 8.0 | 71% – 80% | Very Good |
| B2 | 7 | 6.1 – 7.0 | 61% – 70% | Good |
| C1 | 6 | 5.1 – 6.0 | 51% – 60% | Satisfactory |
| C2 | 5 | 4.1 – 5.0 | 41% – 50% | Average |
| D | 4 | 3.5 – 4.0 | 33% – 40% | Below Average |
| E1 / E2 | – | < 3.5 | < 33% | Needs Improvement |
CGPA in Worldwide Universities
In international universities (like the US, Canada, or Europe), GPA and CGPA are key metrics used in:
-
College admissions
-
Internship eligibility
-
Academic probation or honors programs
Many universities use a 4.0 GPA scale, so Indian students often need to convert their CGPA accordingly when applying abroad.
CGPA and GPA? are they same?
One of the most common questions students have is: “Are CGPA and GPA the same thing?” While they may seem similar, there are key differences in meaning, usage, and calculation, especially when you’re applying for international universities or jobs.
Let’s break it down:
| Criteria | CGPA (Cumulative Grade Point Average) | GPA (Grade Point Average) |
|---|---|---|
| Full Form | Cumulative Grade Point Average | Grade Point Average |
| Usage | Common in India, Pakistan, and other Asian countries | Common in the United States, Canada, Australia, etc. |
| Duration Covered | Reflects performance across an academic year or entire course | Measures performance for one term, semester, or year |
| Scale | Usually calculated on a 10-point scale | Calculated on a 4-point scale (some use 5 or 12) |
| Purpose | Standardized academic evaluation in Indian institutions | Used for admissions, honors, and scholarships abroad |
| Decimal Accuracy | Typically shows up to 1 decimal point (e.g., 8.6) | Often displayed up to 2 decimal points (e.g., 3.75) |
| Percentage Conversion | Follows a fixed formula (e.g., CGPA × 9.5) | Depends on letter grades like A+, B-, C, etc. |
Detailed Explanation:
What is CGPA?
CGPA (Cumulative Grade Point Average) is widely used in India, especially in school boards like CBSE and many universities. It reflects the average grade points earned across all subjects over a year or full program, not just one semester.
For example, a CGPA of 9.0 generally indicates an overall score of 85.5% (when multiplied by 9.5).
What is GPA?
GPA (Grade Point Average) is a grading metric used internationally. It calculates the average of your grades in a specific semester. In most systems, each letter grade (A, B, C, etc.) is assigned a numerical value:
| Grade | Points (4.0 scale) |
|---|---|
| A | 4.0 |
| B | 3.0 |
| C | 2.0 |
| D | 1.0 |
| F | 0.0 |
So, if a student takes 5 courses in one semester and scores 3 A’s and 2 B’s, their GPA will be:
GPA = (4 + 4 + 4 + 3 + 3) / 5 = 3.6
CGPA to GPA Conversion (For International Students)
There is no direct universal formula to convert CGPA to GPA, because:
-
CGPA uses a 10-point scale, while GPA uses 4-point scale
-
GPA depends on credit hours and course weightage
-
Universities may have different grading standards
Still, as a general approximate conversion:
| CGPA (10-point) | GPA (4-point) |
|---|---|
| 9.0 – 10 | 3.7 – 4.0 |
| 8.0 – 8.9 | 3.3 – 3.6 |
| 7.0 – 7.9 | 2.7 – 3.2 |
| 6.0 – 6.9 | 2.0 – 2.6 |
| Below 6.0 | Below 2.0 |
FAQs on CGPA
1. What Is CGPA Multiplying Factor?
The CGPA multiplying factor is used to convert individual course grades into a cumulative grade point average (CGPA). It varies depending on the grading system used by the institution.
2. How Important Is CGPA for Admissions?
CGPA is often an important factor for admissions to further education programs or for certain job opportunities, as it serves as a measure of academic performance and potential.
3. How Does CGPA Impact Career Prospects?
CGPA can impact career prospects by influencing opportunities for further education, scholarships, internships, and job offers. Many employers and educational institutions consider CGPA as an indicator of a candidate’s academic capability and dedication.
4. Is It Possible to Improve CGPA If It Is Low?
Yes, it’s possible to improve a low CGPA through various means such as seeking help from tutors, improving study habits, retaking courses if permitted, focusing on high-value courses, and maintaining consistency in academic performance.
5. What Is a Good CGPA Range to Aim for?
A good CGPA range to aim for can vary depending on your academic goals, the competitiveness of the field you’re interested in, and the standards of the institutions you’re applying to. Generally, aiming for a CGPA above 8.0 (on a 10.0 scale) is considered favorable for many opportunities.
6. How Often Is CGPA Updated in Academic Records?
CGPA is typically updated at the end of each semester or academic term when grades for all courses are finalized and recorded.
7. Can I Calculate My Own CGPA Using My Grades?
Yes, you can calculate your own CGPA using your grades by multiplying the grade points for each course by the course credits, summing them up, and dividing by the total number of credits. Each institution may have its own specific formula for CGPA calculation.
8. Are There Any Specific Strategies to Maintain a High CGPA Throughout the Academic Year?
Strategies to maintain a high CGPA include:
- staying organized,
- attending classes regularly,
- actively participating in discussions,
- seeking help when needed,
- managing time effectively,
- reviewing course materials regularly,
- setting realistic goals,
- and maintaining a healthy balance between academics and personal life.
Additionally, seeking feedback from professors and adjusting study strategies accordingly can also be beneficial.
9. How much CGPA is considered good?
A CGPA above 8.0 (equivalent to ~76%) is generally considered excellent.
10. What is the CGPA full form in Hindi?
CGPA का फुल फॉर्म है: Cumulative Grade Point Average
The post CGPA Full Form: Meaning, Importance, and Calculation in 2025 appeared first on Eduexa.
Page processed in 3.925 seconds.
Powered by SimplePie 1.3.1, Build 20121030175403. Run the SimplePie Compatibility Test. SimplePie is © 2004–2025, Ryan Parman and Geoffrey Sneddon, and licensed under the BSD License.